Dynamic reconfiguration of structural and functional connectivity across core neurocognitive brain networks with development
- PMID: 22171056
- PMCID: PMC3641286
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4465-11.2011
Dynamic reconfiguration of structural and functional connectivity across core neurocognitive brain networks with development
Abstract
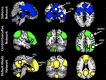
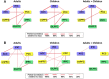
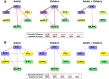
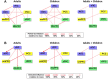
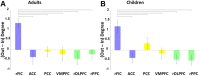
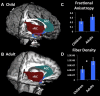
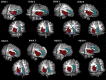
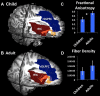
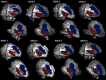
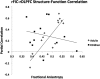
Brain structural and functional development, throughout childhood and into adulthood, underlies the maturation of increasingly sophisticated cognitive abilities. High-level attentional and cognitive control processes rely on the integrity of, and dynamic interactions between, core neurocognitive networks. The right fronto-insular cortex (rFIC) is a critical component of a salience network (SN) that mediates interactions between large-scale brain networks involved in externally oriented attention [central executive network (CEN)] and internally oriented cognition [default mode network (DMN)]. How these systems reconfigure and mature with development is a critical question for cognitive neuroscience, with implications for neurodevelopmental pathologies affecting brain connectivity. Using functional and effective connectivity measures applied to fMRI data, we examine interactions within and between the SN, CEN, and DMN. We find that functional coupling between key network nodes is stronger in adults than in children, as are causal links emanating from the rFIC. Specifically, the causal influence of the rFIC on nodes of the SN and CEN was significantly greater in adults compared with children. Notably, these results were entirely replicated on an independent dataset of matched children and adults. Developmental changes in functional and effective connectivity were related to structural connectivity along these links. Diffusion tensor imaging tractography revealed increased structural integrity in adults compared with children along both within- and between-network pathways associated with the rFIC. These results suggest that structural and functional maturation of rFIC pathways is a critical component of the process by which human brain networks mature during development to support complex, flexible cognitive processes in adulthood.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander DC, Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ, Gee JC. Spatial transformations of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2001;20:1131–1139. - PubMed
-
- Bammer R, Auer M, Keeling SL, Augustin M, Stables LA, Prokesch RW, Stollberger R, Moseley ME, Fazekas F. Diffusion tensor imaging using single-shot SENSE-EPI. Magn Reson Med. 2002;48:128–136. - PubMed
-
- Barnea-Goraly N, Menon V, Eckert M, Tamm L, Bammer R, Karchemskiy A, Dant CC, Reiss AL. White matter development during childhood and adolescence: a cross-sectional diffusion tensor imaging study. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:1848–1854. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed. 1995;8:333–344. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B. 1996;111:209–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
