Preparation, characterization, and biological properties of β-glucans
- PMID: 22171300
- PMCID: PMC3217690
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-4040.82953
Preparation, characterization, and biological properties of β-glucans
Abstract
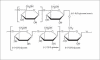
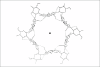
β-Glucans are soluble fibers with physiological functions, such as, interference with absorption of sugars and reduction of serum lipid levels. β-glucans are found in different species, such as, Rhynchelytrum repens, Lentinus edodes, Grifola frondosa, Tremella mesenterica, Tremella aurantia, Zea may, Agaricus blazei, Phellinus baummi, Saccharomyces cerevisae (yeast), and Agaricus blazei murell (mushroom). Analysis of the fractions reveals the presence of arabinose, glucose, xylose, and traces of rhamnose and galactose. The presence of β-glucan in these fractions is confirmed by hydrolyzing the polymers with endo-β-glucanase from Bacillus subtilis, followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of the characteristic oligosaccharides produced. The 4 M KOH fractions from different tissues are subjected to gel permeation chromatography on Sepharose 4B, with separation of polysaccharides, with different degrees of polymerization, the highest molecular mass (above 2000 kDa) being found in young leaves. The molecular mass of the leaf blade polymers is similar (250 kDa) to that of the maize coleoptiles β-glucan used for comparison. The 4 M KOH fraction injected into rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes has shown hypoglycemic activity, reducing blood sugar to normal levels for approximately 24 hours. This performance is better than that obtained with pure β-glucan from barley, which decreases blood sugar levels for about four hours. These results suggest that the activity of β-glucans is responsible for the use of this plant extract as a hypoglycemic drug in folk medicine.
Keywords: Cell wall; diabetes mellitus; grasses; hypoglycemic activity; rhynchelytrum repens; β-glucans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Natural Standard Bottom Line Monograph, Copyright © 2009. [Last accessed on 2011 Feb 25]. Available from: http://www.naturalstandard.com .
-
- Buckeridge MS, Rayon C, Urbanowicz B, Tiné MAS, Carpita NC. Mixed linkage (1,3-1,4) ß-D glucan of grasses. international archival journal. 2003;81:115–27.
-
- Anderson JW, Akanji AO. Treatment of diabetes with high fiber diet. In: Spiller GA, editor. Handbook of Dietary Fiber in Human Nutrition. Ist ed. USA Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1993. pp. 225–7.
-
- Anderson JW, Story L, Sieling B, Chen WJ, Petro MS, Story J. Hypocholesterolemic effect of oat bran or bean intake for hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984;40:1146–55. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JW, Gustafson NJ. Hypocholesterolemic effects of oat and bean products. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988;48:749–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources