An exploration of salivation patterns in normal weight and obese children
- PMID: 22172456
- PMCID: PMC3650916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.appet.2011.11.027
An exploration of salivation patterns in normal weight and obese children
Abstract
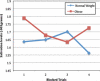
We examined whether children's changes in salivary habituation to food vary based on weight status and/or allocating attention to a task. Children (31 non-overweight and 26 obese, ages 9-12 year) were presented with nine trials of a food stimulus and either listened to an audiobook (attention-demanding) or white noise (no-attention control). The salivary pattern differed significantly by weight status but not by condition or a condition by weight status interaction. This is the first study of salivary habituation in obese children; findings dovetail with an emerging set of evidence that obese individuals display distinctive biological responses to food.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of allocation of attention on habituation to olfactory and visual food stimuli in children.Physiol Behav. 2005 Feb 15;84(2):313-9. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.12.009. Epub 2005 Jan 16. Physiol Behav. 2005. PMID: 15708783
-
Salivary habituation to food stimuli in successful weight loss maintainers, obese and normal-weight adults.Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 Mar;34(3):593-6. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2009.267. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20010900 Free PMC article.
-
Habituation of salivation and motivated responding for food in children.Appetite. 2003 Dec;41(3):283-9. doi: 10.1016/s0195-6663(03)00106-5. Appetite. 2003. PMID: 14637327 Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of oral processing, food perception and social aspects on food consumption: a review.J Oral Rehabil. 2016 Aug;43(8):630-48. doi: 10.1111/joor.12395. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Oral Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 27061099 Review.
-
Family environmental factors influencing the developing behavioral controls of food intake and childhood overweight.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001 Aug;48(4):893-907. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(05)70347-3. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11494642 Review.
Cited by
-
Rationale and protocol for translating basic habituation research into family-based childhood obesity treatment: Families becoming healthy together study.Contemp Clin Trials. 2020 Nov;98:106153. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2020.106153. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Contemp Clin Trials. 2020. PMID: 32950645 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bond DS, Raynor HA. Differences in salivary habituation to a taste stimulus in bariatric surgery candidates and normal weight controls. Obesity Surgery. 2009;19:873–878. - PubMed
-
- Dobson KS, Dozois DJA. Attentional biases in eating disorders. A meta-analytic review of Stroop performance. Clinical Psychology Review. 2002;23:1001–1022. - PubMed
-
- Epstein LH, Mitchell SL, Caggiula AR. The effect of subjective and physiological arousal on dishabituation of salivation. Physiology and Behavior. 1993;53(3):593–597. - PubMed
-
- Epstein LH, Myers MD, Raynor HA, Saelens BE. Treatment of pediatric obesity. Pediatrics. 1997;101:554–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical