Probing the helical tilt and dynamic properties of membrane-bound phospholamban in magnetically aligned bicelles using electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy
- PMID: 22172806
- PMCID: PMC3273594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.11.030
Probing the helical tilt and dynamic properties of membrane-bound phospholamban in magnetically aligned bicelles using electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy
Abstract
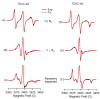
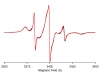
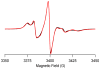
Wild-type phospholamban (WT-PLB), a Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) regulator in the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane, was studied using TOAC nitroxide spin labeling, magnetically aligned bicelles, and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy to ascertain structural and dynamic information. Different structural domains of PLB (transmembrane segment: positions 42 and 45, loop region: position 20, and cytoplasmic domain: position 10) were probed with rigid TOAC spin labels to extract the transmembrane helical tilt and structural dynamic information, which is crucial for understanding the regulatory function of PLB in modulating Ca(2+)-ATPase activity. Aligned experiments indicate that the transmembrane domain of wild-type PLB has a helical tilt of 13°±4° in DMPC/DHPC bicelles. TOAC spin labels placed on the WT-PLB transmembrane domain showed highly restricted motion with more than 100ns rotational correlation time (τ(c)); whereas the loop, and the cytoplasmic regions each consists of two distinct motional dynamics: one fast component in the sub-nanosecond scale and the other component is slower dynamics in the nanosecond range.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation-dependent conformational switch in spin-labeled phospholamban bound to SERCA.J Mol Biol. 2006 May 12;358(4):1032-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.051. Epub 2006 Mar 9. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16574147
-
Electron paramagnetic resonance reveals a large-scale conformational change in the cytoplasmic domain of phospholamban upon binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase.Biochemistry. 2004 May 18;43(19):5842-52. doi: 10.1021/bi035749b. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15134458
-
Phospholamban structural dynamics in lipid bilayers probed by a spin label rigidly coupled to the peptide backbone.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Oct 5;101(40):14437-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402801101. Epub 2004 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15448204 Free PMC article.
-
Probing topology and dynamics of the second transmembrane domain (M2δ) of the acetyl choline receptor using magnetically aligned lipid bilayers (bicelles) and EPR spectroscopy.Chem Phys Lipids. 2017 Aug;206:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2017.05.010. Epub 2017 May 29. Chem Phys Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28571787 Free PMC article.
-
Direct spectroscopic detection of molecular dynamics and interactions of the calcium pump and phospholamban.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Sep 16;853:186-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb08266.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 10603946 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of bicelle lipid composition and temperature for EPR spectroscopy of aligned membranes.J Magn Reson. 2015 Jan;250:71-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2014.09.026. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Magn Reson. 2015. PMID: 25514061 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbations of Native Membrane Protein Structure in Alkyl Phosphocholine Detergents: A Critical Assessment of NMR and Biophysical Studies.Chem Rev. 2018 Apr 11;118(7):3559-3607. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00570. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29488756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The magic of bicelles lights up membrane protein structure.Chem Rev. 2012 Nov 14;112(11):6054-74. doi: 10.1021/cr300061w. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Chem Rev. 2012. PMID: 22920148 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A bifunctional spin label reports the structural topology of phospholamban in magnetically-aligned bicelles.J Magn Reson. 2016 Jan;262:50-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 12. J Magn Reson. 2016. PMID: 26720587 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the interaction of Arg9Cys mutated phospholamban with phospholipid bilayers by solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1828(11):2444-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23850636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fuji J, Ueno A, Kitano K, Tanaka S, Kadoma M, Tada M. Characterization of structural unit of phospholamban by amino acid sequencing and electropherotic analysis. Biochim Biophys Res Commn. 1987;138:1044–1050. - PubMed
-
- Li HM, Cocco MJ, Steitz TA, Engelman DM. Conversion of phospholamban into a soluble pentameric helical bundle. Biochemistry. 2001;40:6636–6645. - PubMed
-
- Simmerman HKB, Jones LR. Phospholamban: protein structure, mechanism of action, and role in cardiac function. Physiol Rev. 1998;78:921–947. - PubMed
-
- Kirchberger MA, Tada M, Katz AM. Phospholamban a regulatory protein of the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Recent Adv Stud Card Struct Metab. 1975;5:103–115. - PubMed
-
- James P, Inui M, Tada M, Chiesi M, Carafoli E. Nature and site of phospholamban regulation of the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989;342:90–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

