Matrix proteases in mitochondrial DNA function
- PMID: 22172992
- PMCID: PMC3383373
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.11.008
Matrix proteases in mitochondrial DNA function
Abstract
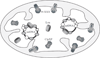
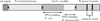
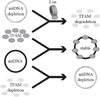
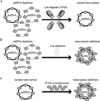
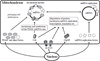
Lon, ClpXP and m-AAA are the three major ATP-dependent proteases in the mitochondrial matrix. All three are involved in general quality control by degrading damaged or abnormal proteins. In addition to this role, they are proposed to serve roles in mitochondrial DNA functions including packaging and stability, replication, transcription and translation. In particular, Lon has been implicated in mtDNA metabolism in yeast, fly and humans. Here, we review the role of Lon protease in mitochondrial DNA functions, and discuss a putative physiological role for mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) degradation by Lon protease. We also discuss the possible roles of m-AAA and ClpXP in mitochondrial DNA functions, and the putative candidate substrates for the three matrix proteases. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Mitochondrial Gene Expression.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ugarte N, Petropoulos I, Friguet B. Oxidized mitochondrial protein degradation and repair in aging and oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;13:539–549. - PubMed
-
- Truscott KN, Lowth BR, Strack PR, Dougan DA. Diverse functions of mitochondrial AAA+ proteins: protein activation, disaggregation, and degradation. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;88:97–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

