Evaluation of aqueductal stenosis by 3D sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions sequence: preliminary results with 3T MR imaging
- PMID: 22173764
- PMCID: PMC8050433
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2833
Evaluation of aqueductal stenosis by 3D sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions sequence: preliminary results with 3T MR imaging
Abstract
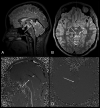
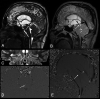
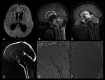
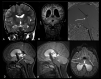
Background and purpose: Diagnosis of AS and periaqueductal abnormalities by routine MR imaging sequences is challenging for neuroradiologists. The aim of our study was to evaluate the utility of the 3D-SPACE sequence with VFAM in patients with suspected AS.
Materials and methods: PC-MRI and 3D-SPACE images were obtained in 21 patients who had hydrocephalus on routine MR imaging scans and had clinical suspicion of AS, as well as in 12 control subjects. Aqueductal patency was visually scored (grade 0, normal; grade 1, partial obstruction; grade 2, complete stenosis) by 2 experienced radiologists on PC-MRI (plus routine T1-weighted and T2-weighted images) and 3D-SPACE images. Two separate scores were statistically compared with each other as well as with the consensus scores obtained from general agreement of both radiologists.
Results: There was an excellent correlation between 3D-SPACE and PC-MRI scores (κ = 0.828). The correlation between 3D-SPACE scorings and consensus-based scorings was higher compared with the correlation between PC-MRI and consensus-based scorings (r = 1, P < .001 and r = 0.966, P < .001, respectively).
Conclusions: 3D-SPACE sequence with VFAM alone can be used for adequate and successful evaluation of the aqueductal patency without the need for additional sequences and examinations. Noninvasive evaluation of the whole cranium is possible in a short time with high resolution by using 3D-SPACE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of spontaneous third ventriculostomy by three-dimensional sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip-angle evolutions (3D-SPACE) sequence by 3T MR imaging: preliminary results with variant flip-angle mode.J Neuroradiol. 2013 Mar;40(1):11-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurad.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Feb 3. J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 22305437 Clinical Trial.
-
Feasibility of 3-dimensional sampling perfection with application optimized contrast sequence in the evaluation of patients with hydrocephalus.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015 May-Jun;39(3):321-8. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000206. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015. PMID: 25978590
-
Assessment of third ventriculostomy patency with the 3D-SPACE technique: a preliminary multicenter research study.J Neurosurg. 2015 Jun;122(6):1347-55. doi: 10.3171/2014.10.JNS14298. Epub 2015 Apr 10. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25859808
-
Evaluation of hydrocephalus patients with 3D-SPACE technique using variant FA mode at 3T.Acta Neurol Belg. 2018 Jun;118(2):169-178. doi: 10.1007/s13760-017-0838-z. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Acta Neurol Belg. 2018. PMID: 28952043 Review.
-
High-resolution 3T MR neurography of the brachial plexus and its branches, with emphasis on 3D imaging.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013 Mar;34(3):486-97. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3287. Epub 2012 Sep 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013. PMID: 22976233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Liliequist membrane by 3D-SPACE technique at 3 T.Neuroradiology. 2016 Jul;58(7):637-47. doi: 10.1007/s00234-016-1669-y. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Neuroradiology. 2016. PMID: 27004925
-
Diagnostic performance of heavily T2-weighted techniques in obstructive hydrocephalus: comparison study of two different 3D heavily T2-weighted and conventional T2-weighted sequences.Jpn J Radiol. 2015 Feb;33(2):94-101. doi: 10.1007/s11604-014-0385-y. Epub 2015 Jan 7. Jpn J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25559932
-
MR assessment of pediatric hydrocephalus: a road map.Childs Nerv Syst. 2016 Jan;32(1):19-41. doi: 10.1007/s00381-015-2888-y. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Childs Nerv Syst. 2016. PMID: 26337698 Review.
-
Heavily T2W 3D-SPACE images for evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid containing spaces.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2012 Jan;22(1):74-5. doi: 10.4103/0971-3026.95410. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22623822 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Assessment of the visual pathways in patients with neurofibromatosis-1 by 3S-space technique with 3-Tesla MRI.Turk J Med Sci. 2019 Dec 16;49(6):1626-1633. doi: 10.3906/sag-1906-14. Turk J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31655505 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan R, Chaseling R, Graf N, et al. . Aqueduct stenosis-benign? J Clin Neurosci 2005;12:178–82 - PubMed
-
- Tisell M. How should primary aqueductal stenosis in adults be treated? A review. Acta Neuro Scand 2005;111:143–53 - PubMed
-
- Algin O, Hakyemez B, Parlak M. Phase-contrast MRI and 3D-CISS versus contrast-enhanced MR cisternography on the evaluation of the aqueductal stenosis. Neuroradiology 2010;52:99–108 - PubMed
-
- Sekerci Z, Akalan N, Kilic C, et al. . Primary non-neoplastic aqueductal stenosis associated with Von Recklinghausen's disease. Turk Neurosurg 1989;1:30–33
-
- Algin O. Role of complex hydrocephalus in unsuccessful endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Childs Nerv Syst 2010;26:3–4 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
