Consensus treatment recommendations for late-onset Pompe disease
- PMID: 22173792
- PMCID: PMC3534745
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.22329
Consensus treatment recommendations for late-onset Pompe disease
Abstract
Introduction: Pompe disease is a rare, autosomal recessive disorder caused by deficiency of the glycogen-degrading lysosomal enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase. Late-onset Pompe disease is a multisystem condition, with a heterogeneous clinical presentation that mimics other neuromuscular disorders.
Methods: Objective is to propose consensus-based treatment and management recommendations for late-onset Pompe disease.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature by a panel of specialists with expertise in Pompe disease was undertaken.
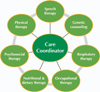
Conclusions: A multidisciplinary team should be involved to properly treat the pulmonary, neuromuscular, orthopedic, and gastrointestinal elements of late-onset Pompe disease. Presymptomatic patients with subtle objective signs of Pompe disease (and patients symptomatic at diagnosis) should begin treatment with enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) immediately; presymptomatic patients without symptoms or signs should be observed without use of ERT. After 1 year of ERT, patients' condition should be reevaluated to determine whether ERT should be continued.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Murphy MK, Black NA, Lamping DL, McKee CM, Sanderson CF, Askham J, et al. Consensus development methods, and their use in clinical guideline development. Health Technol Assess. 1998;2:i–iv. 1–88. - PubMed
-
- Pompe JC. Over idioptische hypertrophie van het hart. Ned Tidschr Geneeskd. 1932;76:304–311.
-
- Kishnani PS, Howell RR. Pompe disease in infants and children. J Pediatr. 2004;144(suppl):S35–S43. - PubMed
-
- Cori GT. Biochemical aspects of glycogen deposition disease. Mod Probl Paediat. 1957;3:344–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

