Galectin-8 in IgA nephritis: decreased binding of IgA by galectin-8 affinity chromatography and associated increased binding in non-IgA serum glycoproteins
- PMID: 22173878
- PMCID: PMC3305883
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-011-9618-3
Galectin-8 in IgA nephritis: decreased binding of IgA by galectin-8 affinity chromatography and associated increased binding in non-IgA serum glycoproteins
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin A nephritis (IgAN) is the most common primary glomerulonephritis worldwide. It is caused by accumulation of IgA1-containing immune complexes in the kidney resulting in renal failure, which is thought to be due to altered glycosylation of IgA with a decrease of 2-3-sialylated galactosides (NeuAcα2-3Gal).
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to analyze whether altered glycosylation of IgA would lead to an altered binding to galectin-8, an endogenous lectin with strong affinity for 2-3-sialylated galactosides. Galectins are a family of β-galactoside-binding proteins; by binding various glycoproteins, they play important roles in the regulation of cellular functions in inflammation and immunity. Hence, an altered binding of IgA to galectin-8 could lead to pathologic immune functions, such as glomerulonephritis.
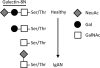
Methods: Affinity chromatography of serum glycoproteins on the human sialogalactoside-binding lectin galectin-8N permitted quantitation of bound and unbound fractions, including IgA.
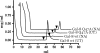
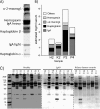
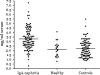
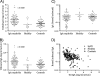
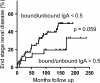
Results: Analysis of ~100 IgA nephritis sera showed that the galectin-8N unbound fraction of IgA increased compared to ~100 controls, consistent with the known loss of galactosylation. A subgroup of ~15% of the IgAN patients had a ratio of galectin-8 bound/unbound IgA <0.09, not found for any of the controls. Unexpectedly, the galectin-8N-binding fraction of serum glycoproteins other than IgA increased in the sera of IgAN patients but not in controls, suggesting a previously unrecognized change in this disease.
Conclusion: This is the first study that relates a galectin, an endogenous lectin family, to IgA nephritis and thus should stimulate new avenues of research into the pathophysiology of the disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different fractions of human serum glycoproteins bind galectin-1 or galectin-8, and their ratio may provide a refined biomarker for pathophysiological conditions in cancer and inflammatory disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1820(9):1366-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.01.007. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22285770
-
Galectin-3 contributes to pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2024 Oct;106(4):658-670. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.06.023. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Kidney Int. 2024. PMID: 39084257
-
Different affinity of galectins for human serum glycoproteins: galectin-3 binds many protease inhibitors and acute phase proteins.Glycobiology. 2008 May;18(5):384-94. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwn015. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Glycobiology. 2008. PMID: 18263896
-
IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schoenlein purpura nephritis: aberrant glycosylation of IgA1, formation of IgA1-containing immune complexes, and activation of mesangial cells.Contrib Nephrol. 2007;157:134-8. doi: 10.1159/000102455. Contrib Nephrol. 2007. PMID: 17495451 Review.
-
Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy.Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1999 Feb;150(2):91-8. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1999. PMID: 10392257 Review.
References
-
- Berger J, Hinglais N. Intercapillary deposits of IgA–IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 1968;74(9):694–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

