Quantitative analyses of antagonism: combinations of midazolam and either flunitrazepam or pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam
- PMID: 22173893
- PMCID: PMC3286322
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.111.188250
Quantitative analyses of antagonism: combinations of midazolam and either flunitrazepam or pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam
Abstract
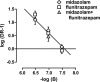
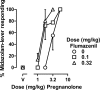
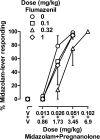
Adverse effects of benzodiazepines limit their clinical use; these effects might be reduced without altering therapeutic effects by administering other positive GABA(A) modulators (i.e., neuroactive steroids) with benzodiazepines. One concern with this strategy involves reversing these combined effects in case of overdose. The current study examined whether flumazenil can attenuate the combined effects of two benzodiazepines, midazolam and flunitrazepam, and the combined effects of midazolam and the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone, in four monkeys discriminating midazolam. Each positive modulator produced ≥80% midazolam-lever responding. Interactions between midazolam and either flunitrazepam or pregnanolone were additive. Flumazenil antagonized the benzodiazepines when they were administered alone or in combination. Schild analyses yielded slopes that did not deviate from unity, regardless of whether benzodiazepines were administered alone or together; the pA(2) value for flumazenil was 7.58. In contrast, flumazenil enhanced the effects of pregnanolone with 0.32 mg/kg flumazenil shifting the pregnanolone dose-effect curve 2-fold leftward. Flumazenil attenuated the combined effects of midazolam and pregnanolone, although antagonism was not dose-dependent. Thus, the interaction between two benzodiazepines was similar to that of a benzodiazepine and a neuroactive steroid; however, flumazenil more efficiently attenuated a combination of two benzodiazepines compared with a combination of a benzodiazepine and a neuroactive steroid. Although the magnitude of antagonism of a benzodiazepine combined with a neuroactive steroid was reduced, these results support continued exploration of the use of combinations of positive modulators to enhance therapeutic effects while reducing adverse effects.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Jan;231(1):181-90. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3218-2. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 23949204 Free PMC article.
-
Negative GABA(A) modulators attenuate the discriminative stimulus effects of benzodiazepines and the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Oct;181(4):697-705. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-0028-1. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15983789
-
Comparing the discriminative stimuli produced by either the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone or the benzodiazepine midazolam in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Mar;214(2):427-35. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2047-9. Epub 2010 Oct 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20972551 Free PMC article.
-
Midazolam and other benzodiazepines.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;(182):335-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-74806-9_16. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18175099 Review.
-
A clinical double-blind study of flumazenil, antagonist of benzodiazepines, in loco-regional anesthesia.Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 1992;43(2):121-9. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 1992. PMID: 1321543 Review.
Cited by
-
Discriminative stimulus effects of pregnanolone in rhesus monkeys.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Jan;231(1):181-90. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3218-2. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 23949204 Free PMC article.
-
Discriminating evidence - use and misuse of the drug-discrimination test in abuse potential assessment of novel CNS drugs.J Psychopharmacol. 2025 Jul;39(7):629-651. doi: 10.1177/02698811251330780. Epub 2025 Apr 17. J Psychopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40243002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute tolerance to chlordiazepoxide qualitatively changes the interaction between flumazenil and pregnanolone and not the interaction between flumazenil and midazolam in rhesus monkeys discriminating midazolam.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 30;700(1-3):159-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.12.028. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23305839 Free PMC article.
-
Differential interactions engendered by benzodiazepine and neuroactive steroid combinations on schedule-controlled responding in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Oct;137:53-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.08.003. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 26255153 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase as a novel approach to high dose diazepam induced hypotension.J Clin Toxicol. 2016 Jun;6(3):1000300. doi: 10.4172/2161-0495.1000300. Epub 2016 May 30. J Clin Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 28255523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dantzer R, Pério A. (1982) Behavioural evidence for partial agonist properties of RO 15-1788, a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 81:655–658 - PubMed
-
- Finn DA, Gallaher EJ, Crabbe JC. (2000) Differential change in neuroactive steroid sensitivity during ethanol withdrawal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:394–405 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

