Effect of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate activated signaling pathways on 1α, 25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulated human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase gene expression in differentiated Caco-2 cells
- PMID: 22174178
- PMCID: PMC4536811
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.24028
Effect of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate activated signaling pathways on 1α, 25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulated human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 24-hydroxylase gene expression in differentiated Caco-2 cells
Abstract
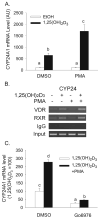
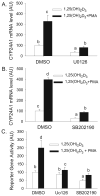
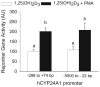
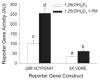
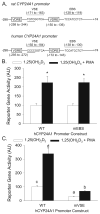
Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), a protein kinase C(PKC) activator, can modulate 1α, 25 dihydroxyvitamin D(3) (1,25(OH)(2)D(3))-induced expression of the 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) gene but this has not been studied in differentiated enterocytes, a primary 1,25(OH)(2) D(3) target cell. We found that in differentiated Caco-2 cells, an established model of the mature absorptive epithelial cell, PMA significantly enhanced 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-induced human CYP24A1 (hCYP24A1) mRNA accumulation and hCYP24A1 promoter-luciferase reporter gene activation by 150%. Reporter gene studies further identified the region between -298 and +74 bp in the hCYP24A1 promoter as critical for the PMA enhancing effect and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis showed that PMA enhanced 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-induced binding of vitamin D receptor to this region. PMA can activate PKC, ERK1/2, and p38 MAP kinases and inhibition of these signaling pathways reduced both 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-induced hCYP24A1 gene transcription and the enhancing effect of PMA. The PMA enhancing effect on 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) action was evident in a minimal promoter with three osteocalcin VDREs and was reduced after mutation of a putative vitamin D stimulatory site in the hCYP24A1 promoter. In contrast, mutation of a Ets binding site (EBS) in the hCYP24A1 promoter had no impact on 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) action or the PMA enhancing effect. These data suggest that in the differentiated enterocyte PMA-induced activation of several signaling pathways contribute to 1,25(OH)(2)D(3)-induced hCYP24A1 gene expression through multiple regulatory motifs within the proximal hCYP24A1 promoter.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
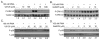
References
-
- Almog T, Naor Z. Mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs) as regulators of spermatogenesis and spermatozoa functions. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 2008;282:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Armbrecht HJ, Boltz MA, Hodam TL, Kumar VB. Differential responsiveness of intestinal epithelial cells to 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D3--role of protein kinase C. J Endocrinol. 2001;169:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Armbrecht HJ, Chen ML, Hodam TL, Boltz MA. Induction of 24-hydroxylase cytochrome P450 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and phorbol exters in normal rat kidney (NRK-52E) cells. J Endocrinol. 1997;153:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Armbrecht HJ, Hodam TL, Boltz MA, Chen ML. Phorbol ester markedly increases the sensitivity of intestinal epithelial cells to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Barletta F, Dhawan P, Christakos S. Integration of hormone signaling in the regulation of human 25(OH)D3 24-hydroxylase transcription. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286:E598–E608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

