Antiproliferative effect of aaptamine on human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells
- PMID: 22174603
- PMCID: PMC3233409
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12117352
Antiproliferative effect of aaptamine on human chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells
Abstract
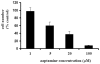
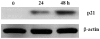
We previously isolated aaptamine, a benzonaphthyridine alkaloid, from marine sponge Aaptos suberitoids. In this study, we investigated the anti-proliferative effect of aaptamine on chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) K562 cells. Aaptamine inhibited growth of K562 with a GI50 as 10 μM, and arrested cell cycle at G2/M phase. Western blot analysis indicated that aaptamine induced p21 expression in K562 cells. Moreover, p21 promoter was activated by aaptamine treatment in p21 transfected K562 cells. Since K562 is p53 negative, aaptamine was demonstrated to be a p53-independent p21 inducer in CML cells.
Keywords: G2/M arrest; K562 cells; aaptamine; p21.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aaptamine, a spongean alkaloid, activates p21 promoter in a p53-independent manner.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Mar 31;342(1):101-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.119. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16480688
-
[Experimental research on tyrosine-kinase inhibitor STI571 and P21WAF gene clone to treat chronic myeloid leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Dec;12(6):737-42. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15631651 Chinese.
-
Proteomic profiling of germ cell cancer cells treated with aaptamine, a marine alkaloid with antiproliferative activity.J Proteome Res. 2012 Apr 6;11(4):2316-30. doi: 10.1021/pr300170p. Epub 2012 Mar 28. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22409352
-
The cytotoxic and mechanistic effects of aaptamine on hepatocellular carcinoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(3):291-7. doi: 10.2174/1871520614666141114201027. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25403168
-
Review on marine sponge alkaloid, aaptamine: A potential antibacterial and anticancer drug.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Jan;99(1):103-110. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13932. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34331335 Review.
Cited by
-
Stellettin B induces apoptosis in human chronic myeloid leukemia cells via targeting PI3K and Stat5.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 25;8(17):28906-28921. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15957. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423649 Free PMC article.
-
Aaptamine Alters Vimentin Expression and Migration Capability of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.J Exp Pharmacol. 2025 May 22;17:239-247. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S512099. eCollection 2025. J Exp Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40420842 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Approaches Versus Approved or Developing Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Therapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 15;11:801779. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.801779. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34993151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sponge-derived alkaloid AP-7 as a sensitizer to cisplatin in the treatment of multidrug-resistant NSCLC via Chk1-dependent mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 9;15:1423684. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423684. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39045048 Free PMC article.
-
New Drugs from the Sea: Pro-Apoptotic Activity of Sponges and Algae Derived Compounds.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jan 7;17(1):31. doi: 10.3390/md17010031. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30621025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Klein A., van Kessel A.G., Grosveld G., Bartram C.R., Hagemeijer A., Bootsma D., Spurr N.K., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Stephenson J.R. A cellular oncogene is translocated to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1982;300:765–767. - PubMed
-
- Radich J.P. Chronic myeloid leukemia 2010: Where are we now and where can we go? Hematology. 2010;2010:122–128. - PubMed
-
- Azam M., Latek R.R., Daley G.Q. Mechanisms of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell. 2003;112:831–843. - PubMed
-
- Melo J.V., Chuah C. Resistance to imatinib mesylate in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Cancer Lett. 2007;249:121–132. - PubMed
-
- Nardi V., Azam M., Daley G.Q. Mechanisms and implications of imatinib resistance mutations in BCR-ABL. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2004;11:35–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

