Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C stabilizes Gemin3 to block p53-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 22174681
- PMCID: PMC3234233
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002418
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C stabilizes Gemin3 to block p53-mediated apoptosis
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Stabilizes Gemin3 to Block p53-mediated Apoptosis.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Apr 30;17(4):e1009556. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009556. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33930100 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
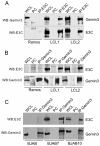
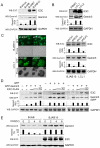
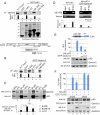
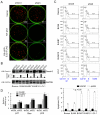
The Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA3C), one of the essential latent antigens for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced immortalization of primary human B lymphocytes in vitro, has been implicated in regulating cell proliferation and anti-apoptosis via interaction with several cellular and viral factors. Gemin3 (also named DDX20 or DP103) is a member of DEAD RNA helicase family which exhibits diverse cellular functions including DNA transcription, recombination and repair, and RNA metabolism. Gemin3 was initially identified as a binding partner to EBNA2 and EBNA3C. However, the mechanism by which EBNA3C regulates Gemin3 function remains unclear. Here, we report that EBNA3C directly interacts with Gemin3 through its C-terminal domains. This interaction results in increased stability of Gemin3 and its accumulation in both B lymphoma cells and EBV transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). Moreover, EBNA3C promotes formation of a complex with p53 and Gemin3 which blocks the DNA-binding affinity of p53. Small hairpin RNA based knockdown of Gemin3 in B lymphoma or LCL cells remarkably attenuates the ability of EBNA3C to inhibit the transcription activity of p53 on its downstream genes p21 and Bax, as well as apoptosis. These findings provide the first evidence that Gemin3 may be a common target of oncogenic viruses for driving cell proliferation and anti-apoptotic activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Burkitt D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg. 1958;46:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus Particles In Cultured Lymphoblasts From Burkitt's Lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;1:702–703. - PubMed
-
- Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields virology, 4th ed. Vol 2, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002. pp. 2575–2627.
-
- zur Hausen H, Schulte-Holthausen H, Klein G, Henle W, Henle G, et al. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970;228:1056–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01CA138434-01A209/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA091792-08/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA138434/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01CA137894-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA091792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067037/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01CA108461-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01AI067037-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE017338/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DE017338-03/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA108461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137894/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

