In Vivo Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- PMID: 22174711
- PMCID: PMC3235887
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/293784
In Vivo Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
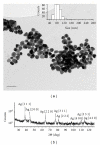
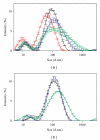
The influence of water chemistry on characterised polyvinyl pyrrolidone- (PVP-) coated silver nanoparticles (81 nm) was investigated. NaCl solution series of 100-800 mg L(-1) lead to initial and temporal increase in nanoparticles size, but agglomeration was limited. pH variation (5-8) had only minor influence on the hydrodynamic particle size. Acute toxicity of nanosivler to zebrafish (Danio rerio) was investigated in a 48-hour static renewal study and compared with the toxicity of silver ions (AgNO(3)). The nanosilver and silver ion 48-hour median lethal concentration (LC(50)) values were 84 μg L(-1) and 25 μg L(-1), respectively. To investigate exposure-related stress, the fish behaviour was observed visually after 0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 27, 30, and 48 hours of both nanosilver and ionic silver treatments. These observations revealed increased rate of operculum movement and surface respiration after nanosilver exposure, suggesting respiratory toxicity. The present study demonstrates that silver nanoparticles are lethal to zebrafish.
Figures

References
-
- Renner H. Ullmann's Encylopedia of Industrial Chemistry. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 2009. Silver, silver compounds, and silver alloys.
-
- Purcell TW, Peters JJ. Sources of silver in the environment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. 1998;17(4):539–546.
-
- Vandevelde T, Renner H, Schlamp G. Ullmann's Encylopedia of Industrial Chemistry. chapter 10. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 2009. Silver, silver compounds, and silver alloys.
-
- Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 2004;275(1):177–182. - PubMed
-
- Benn TM, Westerhoff P. Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environmental Science and Technology. 2008;42(11):4133–4139. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

