Endogenous interleukin-10 constrains Th17 cells in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 22176654
- PMCID: PMC3264534
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-217
Endogenous interleukin-10 constrains Th17 cells in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
Background: Th17 cells play a role in inflammation. Interleukin (IL)-10 is a potent anti-inflammatory cytokine. However, it is poorly understood whether and how endogenous IL-10 impacts the development of Th17 cells in human pathologies.
Materials and methods: We examined the relationship between IL-10 and Th17 cells in patients with Crohn's disease and in IL-10-deficient (IL-10-/-) mice. Th17 cells and dendritic cells (DCs) were defined by flow cytometry and evaluated by functional studies.
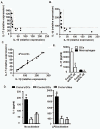
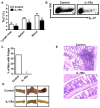
Results: We detected elevated levels of IL-17 and Th17 cells in the intestinal mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease. Intestinal DCs from Crohn's patients produced more IL-1β than controls and were superior to blood DCs in Th17 induction through an IL-1-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, IL-17 levels were negatively associated with those of IL-10 and were positively associated those of IL-1β in intestinal mucosa. These data point toward an in vivo cellular and molecular link among endogenous IL-10, IL-1, and Th17 cells in patients with Crohn's disease. We further investigated this relationship in IL-10(-/-) mice. We observed a systemic increase in Th17 cells in IL-10(-/-) mice when compared to wild-type mice. Similar to the intestinal DCs in patients with Crohn's disease, murine IL-10-/- DCs produced more IL-1β than their wild-type counterparts and promoted Th17 cell development in an IL-1-dependent manner. Finally, in vivo blockade of IL-1 receptor signaling reduced Th17 cell accumulation and inflammation in a mouse model of chemically-induced colitis.
Conclusions: Endogenous IL-10 constrains Th17 cell development through the control of IL-1 production by DCs, and reaffirms the crucial anti-inflammatory role of IL-10 in patients with chronic inflammation.
Figures




References
-
- Tu S, Bhagat G, Cui G, Takaishi S, Kurt-Jones EA, Rickman B, Betz KS, Penz-Oesterreicher M, Bjorkdahl O, Fox JG, Wang TC. Overexpression of interleukin-1beta induces gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:408–419. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.10.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kryczek I WK, Zhao E, Wei S, Vatan L, Szeliga W, Huang E, Greenson J, Chang A, Roliński J, Radwan P, Fang J, Wang G, Zou W. IL-17+ Regulatory T Cells in the Microenvironments of Chronic Inflammation and Cancer. Journal of Immunology. 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

