The psychopath magnetized: insights from brain imaging
- PMID: 22177031
- PMCID: PMC4034374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.11.008
The psychopath magnetized: insights from brain imaging
Abstract
Psychopaths commit a disproportionate amount of violent crime, and this places a substantial economic and emotional burden on society. Elucidation of the neural correlates of psychopathy may lead to improved management and treatment of the condition. Although some methodological issues remain, the neuroimaging literature is generally converging on a set of brain regions and circuits that are consistently implicated in the condition: the orbitofrontal cortex, amygdala, and the anterior and posterior cingulate and adjacent (para)limbic structures. We discuss these findings in the context of extant theories of psychopathy and highlight the potential legal and policy implications of this body of work.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
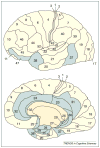
References
-
- Cleckley H. The Mask of Sanity: An Attempt to Reinterpret the So-Called Psychopathic Personality. Mosby; 1941.
-
- Leistico AR, et al. A large-scale meta-analysis relating the Hare measures of psychopathy to antisocial conduct. Law Hum Behav. 2008;32:28–45. - PubMed
-
- Walters GD. Predicting institutional adjustment and recidivism with the psychopathy checklist factor scores: a meta-analysis. Law Hum Behav. 2003;27:541–558. - PubMed
-
- Hemphill JF, et al. Psychopathy and recidivism: a review. Legal Criminol Psychol. 1998;3:139–170.
-
- Gretton H, et al. Psychopathy and recidivism in adolescent sex offenders. Crim Justice Behav. 2001;28:427–449.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

