Spinal radiosurgery--efficacy and safety after prior conventional radiotherapy
- PMID: 22177519
- PMCID: PMC3264666
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-173
Spinal radiosurgery--efficacy and safety after prior conventional radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: Conventional external beam radiotherapy is a standard procedure for treatment of spinal metastases. In case of progression spinal cord tolerance limits further radiotherapy in pre-irradiated areas. Spinal stereotactic radiotherapy is a non-invasive option to re-treat pre-irradiated patients. Nevertheless, spinal radiosurgery results in relevant dose deposition within the myelon with potential toxicity. Aim of the study was to retrospectively analyse the efficacy and feasibility for salvage radiosurgery of spinal metastases.
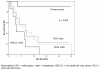
Methods: During a period of 4 years (2005-2009) 70 lesions in 54 patients were treated in 60 radiosurgery sessions and retrospectively analysed. Clinical (pain, sensory and motor deficit) and radiological (CT/MRI) follow-up data were collected prospectively after radiosurgery. Pain - as main symptom - was classified by the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score. Every patient received single session radiosurgery after having been treated first-line with conventionally fractionated radiotherapy. Kaplan-Meier method and life tables were used to analyse freedom from local failure and overall survival.
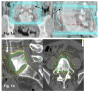
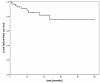
Results: At a median follow-up of 14.5 months the actuarial rates of freedom from local failure at 6/12/18 months were 93%, 88% and 85%, respectively. The median radiosurgery dose was 1 × 18 Gy (range 10-28 Gy) to the median 70% isodose. The VAS score of patients with pain (median 6) dropped significantly (median 4, p = 0.002). In 6 out of 7 patients worse sensory or motor deficit after SRS was caused by local or distant failures (diagnosed by CT/MRI). One patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma developed a progressive complete paraparesis one year after the last treatment at lumbar level L3. Due to multiple surgery and radiosurgery treatments at the lumbar region and further local progression, the exact reason remained unclear. Apart from that, no CTC grade III or higher toxicity has been observed.
Conclusions: By applying spinal radiosurgery relevant radiation doses can be limited to small parts of the myelon. This prevents myelopathic side effects and makes it an effective and safe treatment option for well-suited patients. Especially for previously irradiated patients with local failure or pain salvage SRS represents a valuable treatment option with high local control rates, low toxicity and significant pain reduction.
Figures
References
-
- Arcangeli G, Giovinazzo G, Saracino B, D'Angelo L, Giannarelli D, Micheli A. Radiation therapy in the management of symptomatic bone metastases: the effect of total dose and histology on pain relief and response duration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1998;42(5):1119–1126. - PubMed
-
- Rades D, Stalpers LJ, Veninga T, Schulte R, Hoskin PJ, Obralic N, Bajrovic A, Rudat V, Schwarz R, Hulshof MC. et al.Evaluation of five radiation schedules and prognostic factors for metastatic spinal cord compression. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(15):3366–3375. - PubMed
-
- Baba F, Shibamoto Y, Tomita N, Ikeya-Hashizume C, Oda K, Ayakawa S, Ogino H, Sugie C. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer and small lung metastasis: evaluation of an immobilization system for suppression of respiratory tumor movement and preliminary results. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:15. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hurkmans CW, Cuijpers JP, Lagerwaard FJ, Widder J, van der Heide UA, Schuring D, Senan S. Recommendations for implementing stereotactic radiotherapy in peripheral stage IA non-small cell lung cancer: report from the Quality Assurance Working Party of the randomised phase III ROSEL study. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:1. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

