Regulation of calcium in pancreatic α- and β-cells in health and disease
- PMID: 22177710
- PMCID: PMC3334273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.11.006
Regulation of calcium in pancreatic α- and β-cells in health and disease
Abstract
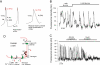
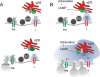
The glucoregulatory hormones insulin and glucagon are released from the β- and α-cells of the pancreatic islets. In both cell types, secretion is secondary to firing of action potentials, Ca(2+)-influx via voltage-gated Ca(2+)-channels, elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) and initiation of Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis. Here we discuss the mechanisms that underlie the reciprocal regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion by changes in plasma glucose, the roles played by different types of voltage-gated Ca(2+)-channel present in α- and β-cells and the modulation of hormone secretion by Ca(2+)-dependent and -independent processes. We also consider how subtle changes in Ca(2+)-signalling may have profound impact on β-cell performance and increase risk of developing type-2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
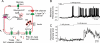

Similar articles
-
Characteristics and functions of {alpha}-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptors expressed in mouse pancreatic {alpha}-cells.Endocrinology. 2010 Apr;151(4):1541-50. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0362. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20189997 Free PMC article.
-
CART is overexpressed in human type 2 diabetic islets and inhibits glucagon secretion and increases insulin secretion.Diabetologia. 2016 Sep;59(9):1928-37. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4020-6. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27338624
-
Inhibition of pancreatic β-cell Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II reduces glucose-stimulated calcium influx and insulin secretion, impairing glucose tolerance.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 2;289(18):12435-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.562587. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24627477 Free PMC article.
-
Role of High Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channel Subunits in Pancreatic β-Cell Insulin Release. From Structure to Function.Cells. 2021 Aug 6;10(8):2004. doi: 10.3390/cells10082004. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
'Resistance is futile?' - paradoxical inhibitory effects of KATP channel closure in glucagon-secreting α-cells.J Physiol. 2020 Nov;598(21):4765-4780. doi: 10.1113/JP279775. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32716554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole genome SNP genotyping and exome sequencing reveal novel genetic variants and putative causative genes in congenital hyperinsulinism.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 15;8(7):e68740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068740. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23869231 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive glucose stimulation of islet beta cells reveals a transition from segregated to integrated modular functional connectivity patterns.Sci Rep. 2015 Jan 19;5:7845. doi: 10.1038/srep07845. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25598507 Free PMC article.
-
Control of insulin secretion by cholinergic signaling in the human pancreatic islet.Diabetes. 2014 Aug;63(8):2714-26. doi: 10.2337/db13-1371. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24658304 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Pancreatic Alpha and Beta Cells Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Life (Basel). 2020 Dec 14;10(12):348. doi: 10.3390/life10120348. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33327428 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Renin Release, a Crucial Event in Homeostasis, is Mediated by Coordinated Calcium Oscillations within Juxtaglomerular Cell Clusters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 21:2024.12.23.629519. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.23.629519. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39763801 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Zimmet P., Alberti K.G., Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature. 2001;414:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Dunning B.E., Foley J.E., Ahren B. Alpha cell function in health and disease: influence of glucagon-like peptide-1. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1700–1713. - PubMed
-
- Gromada J., Franklin I., Wollheim C.B. Alpha-cells of the endocrine pancreas: 35 years of research but the enigma remains. Endocr. Rev. 2007;28:84–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

