uPA and uPAR shRNA inhibit angiogenesis via enhanced secretion of SVEGFR1 independent of GM-CSF but dependent on TIMP-1 in endothelial and glioblastoma cells
- PMID: 22177802
- PMCID: PMC3268919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2011.11.008
uPA and uPAR shRNA inhibit angiogenesis via enhanced secretion of SVEGFR1 independent of GM-CSF but dependent on TIMP-1 in endothelial and glioblastoma cells
Abstract
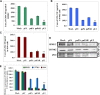
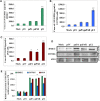
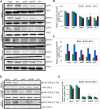
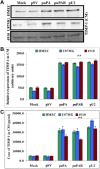
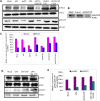
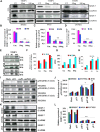
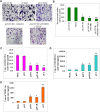
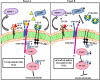
The uPA/uPAR system is known to play a critical role in angiogenesis of glioblastoma. Previously, we have shown that shRNA against uPA and uPAR attenuates angiogenesis by blocking nuclear translocation of angiogenin, inhibition of angiopoietin/Tie2 signaling, and regulating several other pro-angiogenic, angiostatic and anti-angiogenic molecules. Further analysis revealed that GM-CSF, a pleiotropic cytokine, was significantly inhibited in U87MG and 4910 co-cultures with endothelial cells transfected with shRNA against uPA and uPAR. The role of the uPA/uPAR system in this process is not completely understood. Analysis of tumor conditioned medium of U87MG, 4910 and HMECs transfected with shRNA against uPA or uPAR alone or in combination (pU2) revealed inhibition of GM-CSF-enhanced secretion of SVEGFR1 as shown by Western blotting and ELISA. Moreover, phosphorylation of JAK2 and STAT5, the downstream effectors of GM-CSF signaling, was also inhibited in all three cell lines. Phosphorylation at Tyr 166 position of the GM-CSFRβ subunit, the signal activating subunit of the GM-CSF receptor, was inhibited in HMEC, U87MG and 4910 cells. Further analysis revealed that shRNA against uPA and/or uPAR increased secretion of TIMP-1, which is known to enhance SVEGFR1 secretion in endothelial cells. Moreover, addition of purified uPA (with and without GM-CSF) activated JAK2/STAT5 signaling in HMEC. Exogenous addition of SVEGFR1 to pU2 tumor conditioned medium enhanced inhibition of VEGF-induced endothelial capillary tube formation as assessed by an in vitro angiogenesis assay. To determine the significance of these events in vivo, nude mice with pre-established tumors treated with shRNA against uPA and/or uPAR showed decreased levels of GM-CSF and increased levels of SVEGFR1 and TIMP-1 when compared with controls. Enhanced secretion of SVEGFR1 by puPA, puPAR and pU2 in endothelial and GBM cells was mediated indirectly by MMP-7 and augmented by ectodomain shedding of VEGFr1 by tyrosine phosphorylation at the 1213 position. Taken together, these results suggest that the uPA/uPAR system could prove beneficial as an indirect target for inhibition of angiogenesis in glioblastoma.
Copyright © 2011 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of uPA and uPAR attenuates angiogenin mediated angiogenesis in endothelial and glioblastoma cell lines.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 27;5(8):e12458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012458. PLoS One. 2010. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2025 Aug 14;20(8):e0330088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330088. PMID: 20805979 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Specific knockdown of uPA/uPAR attenuates invasion in glioblastoma cells and xenografts by inhibition of cleavage and trafficking of Notch -1 receptor.Mol Cancer. 2011 Oct 17;10:130. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-130. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22004682 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-4 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mediates the upregulation of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 in RAW264.7 cells-a process in which p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling has an important role.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016 Jun;49(3):344-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.06.008. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016. PMID: 25132397
-
Mechanisms by which cleaved kininogen inhibits endothelial cell differentiation and signalling.Thromb Haemost. 2010 Nov;104(5):875-85. doi: 10.1160/TH10-01-0017. Epub 2010 Sep 30. Thromb Haemost. 2010. PMID: 20886177 Review.
-
VEGF-initiated angiogenesis and the uPA/uPAR system.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Nov-Dec;6(6):535-615. doi: 10.4161/cam.22243. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 23076133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of apoptosis through extrinsic/intrinsic pathways and suppression of ERK/NF-κB signalling participate in anti-glioblastoma of imipramine.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(7):3982-4000. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15022. Epub 2020 Mar 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32149465 Free PMC article.
-
poFUT1 promotes uterine angiogenesis and vascular remodeling via enhancing the O-fucosylation on uPA.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Oct 10;10(10):775. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2005-3. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31601791 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating biomarkers in high-grade gliomas: current insights and future perspectives.J Neurooncol. 2025 Mar;172(1):41-49. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04903-z. Epub 2024 Dec 13. J Neurooncol. 2025. PMID: 39671020 Review.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) as a therapeutic target in cancer.J Transl Med. 2022 Mar 18;20(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03329-3. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35303878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SCO-spondin oligopeptide inhibits angiogenesis in glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 12;8(49):85969-85983. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20837. eCollection 2017 Oct 17. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29156770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behzadian, M.A. , Windsor, L.J. , Ghaly, N. , Liou, G. , Tsai, N.T. , Caldwell, R.B. , 2003. VEGF-induced paracellular permeability in cultured endothelial cells involves urokinase and its receptor. FASEB J.. 17, 752–754. - PubMed
-
- Bene, M.C. , Castoldi, G. , Knapp, W. , Rigolin, G.M. , Escribano, L. , Lemez, P. , 2004. CD87 (urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor), function and pathology in hematological disorders: a review. Leukemia. 18, 394–400. - PubMed
-
- Binder, B.R. , Mihaly, J. , Prager, G.W. , 2007. uPAR-uPA-PAI-1 interactions and signaling: a vascular biologist's view. Thromb. Haemost.. 97, 336–342. - PubMed
-
- Blasi, F. , Carmeliet, P. , 2002. uPAR: a versatile signalling orchestrator. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.. 3, 932–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

