Th17 cells induce ectopic lymphoid follicles in central nervous system tissue inflammation
- PMID: 22177922
- PMCID: PMC3422678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.10.015
Th17 cells induce ectopic lymphoid follicles in central nervous system tissue inflammation
Abstract
Ectopic lymphoid follicles are hallmarks of chronic autoimmune inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, and myasthenia gravis. However, the effector cells and mechanisms that induce their development are unknown. Here we showed that in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the animal model of MS, Th17 cells specifically induced ectopic lymphoid follicles in the central nervous system (CNS). Development of ectopic lymphoid follicles was partly dependent on the cytokine interleukin 17 (IL-17) and on the cell surface molecule Podoplanin (Pdp), which was expressed on Th17 cells, but not on other effector T cell subsets. Pdp was also crucial for the development of secondary lymphoid structures: Pdp-deficient mice lacked peripheral lymph nodes and had a defect in forming normal lymphoid follicles and germinal centers in spleen and lymph node remnants. Thus, Th17 cells are uniquely endowed to induce tissue inflammation, characterized by ectopic lymphoid follicles within the target organ.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
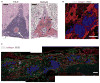

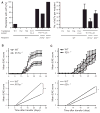
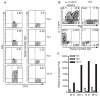
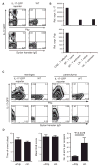
References
-
- Colonna M, Samaridis J, Angman L. Molecular characterization of two novel C-type lectin-like receptors, one of which is selectively expressed in human dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2000;30:697–704. - PubMed
-
- Columba-Cabezas S, Griguoli M, Rosicarelli B, Magliozzi R, Ria F, Serafini B, Aloisi F. Suppression of established experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and formation of meningeal lymphoid follicles by lymphotoxin beta receptor-Ig fusion protein. J Neuroimmunol. 2006;179:76–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 HL066987/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS045937/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL066987-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 089009/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS059996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS035685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01A1044880/PHS HHS/United States
- P01A1039671/PHS HHS/United States
- R37NS030843/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045937/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS059996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01NS038037/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS035685/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

