Vitamin E restriction in the diet enhances phagocytic activation by dichloroacetate and trichloroacetate in mice
- PMID: 22178223
- PMCID: PMC3299817
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.055
Vitamin E restriction in the diet enhances phagocytic activation by dichloroacetate and trichloroacetate in mice
Abstract
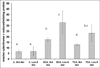
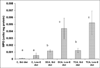
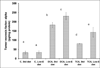
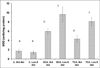
The effects of a vitamin E-restricted diet on the induction of phagocytic activation by dichloroacetate (DCA) and trichloroacetate (TCA) was investigated. Groups of B6C3F1 male mice were either kept on standard diet (Std diet group) or diet that had the vitamin provided only by its natural ingredients (Low-E diet group). The animals in each diet group were administered 77 mg of DCA or TCA/ kg/day, or 5 ml/kg water (controls), by gavage, for 13 weeks. Thereafter, peritoneal lavage cells (PLC) were assayed for superoxide anion (SA), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and myeloperoxidase (MPO), as well as for the activities of the anti-oxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px). SA and TNFα production, as well as MPO, SOD, CAT and GSH-Px activities were significantly increased in the cells from the Low-E diet group treated with the compounds as compared with cells from hosts in the Std-diet group that received the corresponding treatments. The results indicate that consumption of a Vitamin E-restricted diet enhances the induction of phagocytic activation by DCA and TCA, a mechanism that was previously suggested to be an initial adaptive/protective response against the compounds long-term effects.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of a low vitamin E diet on dichloroacetate- and trichloroacetate-induced oxidative stress in the livers of mice.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2012 Mar-Apr;26(4):147-54. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20421. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22447681 Free PMC article.
-
The induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, superoxide anion, myeloperoxidase, and superoxide dismutase in the peritoneal lavage cells of mice after prolonged exposure to dichloroacetate and trichloroacetate.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2010 Mar-Apr;24(2):136-44. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20322. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20391627 Free PMC article.
-
The induction of phagocytic activation by mixtures of the water chlorination by-products, dichloroacetate- and trichloroacetate, in mice after subchronic exposure.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013 Apr;27(4):237-42. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21476. Epub 2013 Feb 21. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23436740 Free PMC article.
-
Mode of action of liver tumor induction by trichloroethylene and its metabolites, trichloroacetate and dichloroacetate.Environ Health Perspect. 2000 May;108 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):241-59. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108s2241. Environ Health Perspect. 2000. PMID: 10807555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in mouse liver tumor induction by trichloroethylene and metabolites.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008;38(10):857-75. doi: 10.1080/10408440802209796. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18821149 Review.
References
-
- Bensoussan K, Morales CR, Hermo L. Vitamin E deficiency causes incomplete spermatogenesis and affects the structural differentiation of epithelial cells of the epidydymis in the rat. J. Androl. 1998;19:266–288. - PubMed
-
- Boxer L. Regulation of phagocyte function by α-tocopherol. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1986;45:333–344. - PubMed
-
- Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1982;78:206–209. - PubMed
-
- Bull RJ, Sanchez IM, Nelson MA, Larson JL, Lansing AJ. Liver tumor induction in B6C3F1 mice by dichloroacetate and dichloroacetate. Toxicology. 1990;63:341–359. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

