Studying microRNAs in the brain: technical lessons learned from the first ten years
- PMID: 22178329
- PMCID: PMC3637683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.12.004
Studying microRNAs in the brain: technical lessons learned from the first ten years
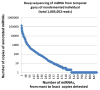
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

