Establishment and characterization of two 5-fluorouracil-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
- PMID: 22179686
- PMCID: PMC3584526
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1300
Establishment and characterization of two 5-fluorouracil-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines
Abstract
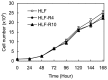
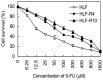
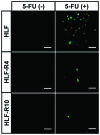
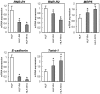
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) chemotherapy is the first choice treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and resistance is the major obstacle to successful treatment. Recent studies have reported that epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is associated with chemoresistance in cancers. We speculated that EMT and 5-FU metabolism are related to the mechanism of 5-FU resistance. First, two 5-FU-resistant cell lines, HLF-R4 and HLF-R10, were established from the HLF undifferentiated human HCC cell line. Whereas cell growth was similar in the HLF and HLF-R cell lines, HLF-Rs are about 4- and 10-fold more resistant compared with the HLF cells; thus, we named these cell lines HLF-R4 and HLF-R10, respectively. The terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling assay also showed a dramatically decreased number of apoptotic cells in the HLF-Rs after treatment with 5-FU. We next assessed the characteristics of the HLF, HLF-R4 and HLF-R10 cells. Consistent with our hypothesis, the HLF-Rs had typical morphologic phenotypes of EMT, loss of cell-cell adhesion, spindle-shaped morphology and increased formation of pseudopodia. Real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction data showed downregulated E-cadherin and upregulated Twist-1 and also indicated that EMT changes occurred in the HLF-Rs. We also found decreased ribonucleotide reductase and increased multidrug resistance protein 5 genes in the HLF-R cells. Our results suggested that the metabolism of EMT and 5-FU has important roles in 5-FU chemoresistance in the HLF-R cells, and that the HLF-R cells would be useful in vitro models for understanding the 5-FU-resistant mechanisms in HCC.
Figures

References
-
- Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137–2150. - PubMed
-
- Wang XN, Han X, Xu LN, Yin LH, Xu YW, Qi Y, Peng JY. Enhancement of apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells through synergy of berberine and evodiamine. Phytomedicine. 2008;15:1062–1068. - PubMed
-
- Ming ZJ, Hu Y, Qiu YH, Cao L, Zhang XG. Synergistic effects of beta-aescin and 5-fluorouracil in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:575–580. - PubMed
-
- Higuchi E, Oridate N, Furuta Y, Suzuki S, Hatakeyama H, Sawa H, Sunayashiki-Kusuzaki K, Yamazaki K, Inuyama Y, Fukuda S. Differentially expressed genes associated with CIS-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) resistance in head and neck cancer using differential display and CDNA microarray. Head Neck. 2003;25:187–193. - PubMed
-
- Scotto KW, Bertino JR. The Molecular Basis of Cancer. 2nd edition. W. B. Sanders; Foster City: 2001. Natural and acquired resistance to chemotherapeutic agents; pp. 407–422.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

