Multivariate analysis of cartilage degradation using the support vector machine algorithm
- PMID: 22179972
- PMCID: PMC3310939
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.23189
Multivariate analysis of cartilage degradation using the support vector machine algorithm
Abstract
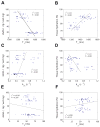
An important limitation in MRI studies of early osteoarthritis is that measured MRI parameters exhibit substantial overlap between different degrees of cartilage degradation. We investigated whether multivariate support vector machine analysis would permit improved tissue characterization. Bovine nasal cartilage samples were subjected to pathomimetic degradation and their T(1), T(2), magnetization transfer rate (k(m) ), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were measured. Support vector machine analysis performed using certain parameter combinations exhibited particularly favorable classification properties. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for detection of extensive and mild degradation were 1.00 and 0.94, respectively, using the set (T(1), k(m), ADC), compared with 0.97 and 0.60 using T(1), the best univariate classifier. Furthermore, a degradation probability for each sample, derived from the support vector machine formalism using the parameter set (T(1), k(m), ADC), demonstrated much stronger correlations (r(2) = 0.79-0.88) with direct measurements of tissue biochemical components than did even the best-performing individual MRI parameter, T(1) (r(2) = 0.53-0.64). These results, combined with our previous investigation of Gaussian cluster-based tissue discrimination, indicate that the combinations (T(1), k(m)) and (T(1), k(m), ADC) may emerge as particularly useful for characterization of early cartilage degradation.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Laurent D, Wasvary J, Rudin M, O’Byrne E, Pellas T. In vivo assessment of macromolecular content in articular cartilage of the goat knee. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49(6):1037–1046. - PubMed
-
- Chen CT, Fishbein KW, Torzilli PA, Hilger A, Spencer RG, Horton WE., Jr Matrix fixed-charge density as determined by magnetic resonance microscopy of bioreactor-derived hyaline cartilage correlates with biochemical and biomechanical properties. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(4):1047–1056. - PubMed
-
- Valerio M, Panebianco V, Sciarra A, Osimani M, Salsiccia S, Casciani L, Giuliani A, Bizzarri M, Di Silverio F, Passariello R, Conti F. Classification of prostatic diseases by means of multivariate analysis on in vivo proton MRSI and DCE-MRI data. NMR In Biomedicine. 2009;22(10):1036–1046. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

