Expression optimization and synthetic gene networks in cell-free systems
- PMID: 22180537
- PMCID: PMC3333853
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr1191
Expression optimization and synthetic gene networks in cell-free systems
Abstract
Synthetic biology offers great promise to a variety of applications through the forward engineering of biological function. Most efforts in this field have focused on employing living cells, yet cell-free approaches offer simpler and more flexible contexts. Here, we evaluate cell-free regulatory systems based on T7 promoter-driven expression by characterizing variants of TetR and LacI repressible T7 promoters in a cell-free context and examining sequence elements that determine expression efficiency. Using the resulting constructs, we then explore different approaches for composing regulatory systems, leading to the implementation of inducible negative feedback in Escherichia coli extracts and in the minimal PURE system, which consists of purified proteins necessary for transcription and translation. Despite the fact that negative feedback motifs are common and essential to many natural and engineered systems, this simple building block has not previously been implemented in a cell-free context. As a final step, we then demonstrate that the feedback systems developed using our cell-free approach can be implemented in live E. coli as well, illustrating the potential for using cell-free expression to fast track the development of live cell systems in synthetic biology. Our quantitative cell-free component characterizations and demonstration of negative feedback embody important steps on the path to harnessing biological function in a bottom-up fashion.
Figures

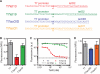
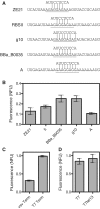
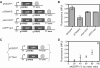
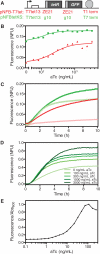
Similar articles
-
Multi-input regulation and logic with T7 promoters in cells and cell-free systems.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 23;8(10):e78442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078442. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24194933 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli σ70 promoters allow expression rate control at the cellular level in genome-integrated expression systems.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 Mar 5;19(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01311-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32138729 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for using integral feedback control to construct a perfectly adapting synthetic gene network.J Theor Biol. 2010 Oct 21;266(4):723-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.07.034. Epub 2010 Aug 3. J Theor Biol. 2010. PMID: 20688080
-
Cell-free synthetic biology for environmental sensing and remediation.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;45:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.01.010. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28226291 Review.
-
Purified cell-free systems as standard parts for synthetic biology.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014 Oct;22:158-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.09.031. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25438802 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-Free Mixing of Escherichia coli Crude Extracts to Prototype and Rationally Engineer High-Titer Mevalonate Synthesis.ACS Synth Biol. 2016 Dec 16;5(12):1578-1588. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00154. Epub 2016 Aug 22. ACS Synth Biol. 2016. PMID: 27476989 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of an entirely in vitro approach for rapid prototyping of DNA regulatory elements for synthetic biology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Mar 1;41(5):3471-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt052. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23371936 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a Transcriptional Biosensor for the Portable, On-Demand Detection of Cyanuric Acid.ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Jan 17;9(1):84-94. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.9b00348. Epub 2019 Dec 26. ACS Synth Biol. 2020. PMID: 31825601 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing a New Fluorescent Protein for a Low Limit of Detection Sensing in the Cell-Free System.ACS Synth Biol. 2022 Aug 19;11(8):2800-2810. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00180. Epub 2022 Jul 19. ACS Synth Biol. 2022. PMID: 35850511 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-input regulation and logic with T7 promoters in cells and cell-free systems.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 23;8(10):e78442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078442. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24194933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endy D. Foundations for engineering biology. Nature. 2005;438:449–453. - PubMed
-
- Purnick PE, Weiss R. The second wave of synthetic biology: from modules to systems. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009;10:410–422. - PubMed
-
- Sprinzak D, Elowitz MB. Reconstruction of genetic circuits. Nature. 2005;438:443–448. - PubMed
-
- Elowitz MB, Leibler S. A synthetic oscillatory network of transcriptional regulators. Nature. 2000;403:335–338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

