Preliminary findings on the interactive effects of IV ethanol and IV nicotine on human behavior and cognition: a laboratory study
- PMID: 22180582
- PMCID: PMC6281082
- DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntr258
Preliminary findings on the interactive effects of IV ethanol and IV nicotine on human behavior and cognition: a laboratory study
Abstract
Introduction: There are mixed reports on nicotine's effects on alcohol-induced impairment in cognitive performance and behavior in humans. The main objective of this study was to characterize the interactive effects of acute intravenous (IV) alcohol and nicotine administration on behavior and cognition in healthy nonsmokers.
Methods: Healthy subjects aged 21-44 years participated in 3 test days. On each test day, they received in a double-blind randomized manner one of three IV alcohol infusion conditions using a "clamp": placebo, targeted breathalyzer of 40 mg%, or targeted breathalyzer of 80 mg%. Alcohol infusion was delivered over 20 min and lasted for 120 min. They also received both placebo and active nicotine in a fixed order delivered intravenously. Placebo nicotine was delivered first over 10 min at the timepoint when the breath alcohol was "clamped"; active nicotine (1.0 mcg/kg/min) was delivered for 10 min, 70 min after the alcohol infusion was clamped. Subjective effects of alcohol were measured using the Biphasic Alcohol Effects Scale and the Number of Drinks Scale. Cognitive inhibition and attention were measured by the Continuous Performance Task-Identical Pairs and working memory by the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Task (RAVLT).
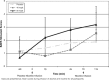
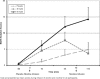
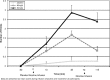
Results: Nicotine significantly reversed subjective intoxication and sedation of alcohol at the low dose. Alcohol impaired performance on the RAVLT, and nicotine further impaired verbal learning and recall at both doses of alcohol.
Conclusions: The data showed that nicotine had an effect on subjective alcohol effects but did not reverse and actually worsened alcohol-induced deficits in memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of family history of alcohol dependence on the subjective response to alcohol using the intravenous alcohol clamp.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Dec;37(12):2011-8. doi: 10.1111/acer.12199. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 23895557 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of nicotine on novelty detection and memory recognition performance: double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of smokers and nonsmokers.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009 Sep;205(4):625-33. doi: 10.1007/s00213-009-1571-y. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19488741 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose-related enhancement of mood and cognition in smokers administered nicotine nasal spray.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Feb;33(3):588-98. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301425. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 17443125 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute alcohol and cognition: Remembering what it causes us to forget.Alcohol. 2019 Sep;79:105-125. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30981807 Review.
-
Effects of the nicotine patch on performance during the first week of smoking cessation.Nicotine Tob Res. 2003 Apr;5(2):169-80. doi: 10.1080/1462220031000074873. Nicotine Tob Res. 2003. PMID: 12745489 Review.
Cited by
-
Prospective Association Between Tobacco Use and at-Risk Alcohol Consumption Among Swedish Adolescents: Outlining the Influence of Tobacco Product, Frequency of Use and Gender in the LoRDIA Cohort.Tob Use Insights. 2024 Oct 30;17:1179173X241298524. doi: 10.1177/1179173X241298524. eCollection 2024. Tob Use Insights. 2024. PMID: 39494130 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine and ethanol co-use in Long-Evans rats: Stimulatory effects of perinatal exposure to a fat-rich diet.Alcohol. 2015 Aug;49(5):479-89. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25979531 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Alcohol Intoxication on Sexual Decision-Making among Men Who Have Sex with Men (MSM): Alcohol's Influences on Self-Control Processes.Clin Psychol Sci. 2023 Jan;11(1):40-58. doi: 10.1177/21677026221079780. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Clin Psychol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36865995 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotine interactions with low-dose alcohol: pharmacological influences on smoking and drinking motivation.J Abnorm Psychol. 2013 Nov;122(4):1154-65. doi: 10.1037/a0034538. J Abnorm Psychol. 2013. PMID: 24364618 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ecological momentary assessment of working memory under conditions of simultaneous marijuana and tobacco use.Addiction. 2016 Aug;111(8):1466-76. doi: 10.1111/add.13342. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Addiction. 2016. PMID: 26857917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ait-Daoud N, Wiesbeck G, Bienkowski P, Li M, Pfutzer R, Singer M, et al. Comorbid alcohol and nicotine dependence: From the biomolecular basis to clinical consequences. Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research. 2005;29:1541–1549. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000174692.20933.49. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JE, Tichauer M, Leyton M, Pihl RO. Nicotine increases alcohol self-administration in non-dependent male smokers. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2006;81:197–204. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2005.06.009. - PubMed
-
- Bobo JK, Huston C. Sociocultural influences on smoking and drinking. Alcohol and Drug Research. 2000;24:225–232. Retrieved from http://www.jsad.com/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burton SM, Tiffany ST. The effect of alcohol consumption on craving to smoke. Addiction. 1997;92:15–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1997.tb03634.x. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso RA, Brozowski SJ, Chavez-Noriega LE, Harpold M, Valenzuela CF, Harris RA. Effects of ethanol on recombinant human neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1999;289:774–780. Retrieved from http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources