Complete genome sequence of Ferroglobus placidus AEDII12DO
- PMID: 22180810
- PMCID: PMC3236036
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.2225018
Complete genome sequence of Ferroglobus placidus AEDII12DO
Abstract
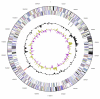
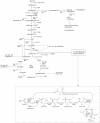
Ferroglobus placidus belongs to the order Archaeoglobales within the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Strain AEDII12DO is the type strain of the species and was isolated from a shallow marine hydrothermal system at Vulcano, Italy. It is a hyperthermophilic, anaerobic chemolithoautotroph, but it can also use a variety of aromatic compounds as electron donors. Here we describe the features of this organism together with the complete genome sequence and annotation. The 2,196,266 bp genome with its 2,567 protein-coding and 55 RNA genes was sequenced as part of a DOE Joint Genome Institute Laboratory Sequencing Program (LSP) project.
Keywords: Archaea; Archaeoglobales; Euryarchaeota; anaerobe; hydrothermal vent; hyperthermophile.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

