Genome sequence of the moderately thermophilic halophile Flexistipes sinusarabici strain (MAS10)
- PMID: 22180813
- PMCID: PMC3236037
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.2235024
Genome sequence of the moderately thermophilic halophile Flexistipes sinusarabici strain (MAS10)
Abstract
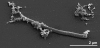
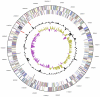
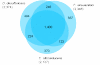
Flexistipes sinusarabici Fiala et al. 2000 is the type species of the genus Flexistipes in the family Deferribacteraceae. The species is of interest because of its isolated phylogenetic location in a genomically under-characterized region of the tree of life, and because of its origin from a multiply extreme environment; the Atlantis Deep brines of the Red Sea, where it had to struggle with high temperatures, high salinity, and a high concentrations of heavy metals. This is the fourth completed genome sequence to be published of a type strain of the family Deferribacteraceae. The 2,526,590 bp long genome with its 2,346 protein-coding and 53 RNA genes is a part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: Deferribacteraceae; GEBA; Gram-negative; brine; heterotrophic; marine; moderately thermophilic; non-motile; strictly anaerobic.
Figures

References
-
- Fiala G, Woese CR, Langworthy TA, Stetter KO. Flexistipes sinusarabici a novel genus and species of eubacteria occurring in the Atlantis II Deep brines of the Red Sea. Arch Microbiol 1990; 154:120-126 10.1007/BF00423320 - DOI
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Bascic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 - PubMed
-
- Korf I, Yandell M, Bedell J. BLAST, O'Reilly, Sebastopol, 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

