Different exercise protocols improve metabolic syndrome markers, tissue triglycerides content and antioxidant status in rats
- PMID: 22182600
- PMCID: PMC3296599
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-3-35
Different exercise protocols improve metabolic syndrome markers, tissue triglycerides content and antioxidant status in rats
Abstract
Background: An increase in the prevalence of obesity entails great expenditure for governments. Physical exercise is a powerful tool in the combat against obesity and obesity-associated diseases. This study sought to determine the effect of three different exercise protocols on metabolic syndrome and lipid peroxidation markers and the activity of antioxidant enzymes in adult Wistar rats (120 days old).
Methods: Animals were randomly divided into four groups: the control (C) group was kept sedentary throughout the study; the aerobic group (A) swam1 h per day, 5 days per week, at 80% lactate threshold intensity; the strength group (S) performed strength training with four series of 10 jumps, 5 days per week; and the Concurrent group (AS) was trained using the aerobic protocol three days per week and the strength protocol two days per week.
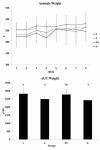
Results: Groups A and S exhibited a reduction in body weight compared to group C. All exercised animals showed a reduction in triglyceride concentrations in fatty tissues and the liver. Exercised animals also exhibited a reduction in lipid peroxidation markers (TBARS) and an increase in serum superoxide dismutase activity. Animals in group A had increased levels of liver catalase and superoxide dismutase activities.
Conclusions: We concluded that all physical activity protocols improved the antioxidant systems of the animals and decreased the storage of triglycerides in the investigated tissues.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of dietary n-6 and n-3 lipids on antioxidant defense system in livers of exercised rats.J Am Coll Nutr. 1998 Dec;17(6):586-94. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1998.10718807. J Am Coll Nutr. 1998. PMID: 9853538
-
Beneficial Effects of Endurance Exercise with Rosmarinus officinalis Labiatae Leaves Extract on Blood Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Lipid Peroxidation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Can J Diabetes. 2015 Jun;39(3):229-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2014.11.003. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Can J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25659282
-
Interaction of hypercaloric diet and physical exercise on lipid profile, oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses.Food Chem Toxicol. 2006 Jul;44(7):1167-72. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.01.004. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16516366
-
Exercise counteracts fatty liver disease in rats fed on fructose-rich diet.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Oct 14;9:116. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-116. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20946638 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of age increment and 36-week exercise training on antioxidant enzymes and apoptosis in rat heart tissue.J Sports Sci Med. 2007 Jun 1;6(2):243-9. eCollection 2007. J Sports Sci Med. 2007. PMID: 24149335 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Swimming training induces liver mitochondrial adaptations to oxidative stress in rats submitted to repeated exhaustive swimming bouts.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055668. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405192 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-endurance training prevents acute alcoholic liver injury in rats through the regulation of damaged mitochondria accumulation and mitophagy balance.Hepatol Int. 2014 Jul;8(3):425-35. doi: 10.1007/s12072-014-9529-5. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Hepatol Int. 2014. PMID: 26202644
-
Prevalence and determinants of metabolic syndrome among women in Chinese rural areas.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036936. Epub 2012 May 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22590636 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Strength Training Prevents Hyperinsulinemia, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation Independent of Weight Loss in Fructose-Fed Animals.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 4;6:31106. doi: 10.1038/srep31106. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27487746 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic training and vitamin D supplementation on glycemic indices and adipose tissue gene expression in type 2 diabetic rats.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 23;13(1):10218. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37489-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37353689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schulz L, Schoeller DA. A compilation of total daily energy expenditures and body weights in healthy adults. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 1994;60:676–681. - PubMed
-
- Hanley AJG, Williams K, Festa A, Wagenknetcht LE, D'Agostino JR, Haffner SM. Markers and development of the metabolic syndrome. The insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes. 2005;54(suppl 1):3140–7. - PubMed
-
- Ervin RB. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults 20 Years of Age and Over, by Sex, Age, Race and Ethnicity, and Body Mass Index: United States. National Health Statistics Reports. 2009;13:1–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

