DHCEO accumulation is a critical mediator of pathophysiology in a Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome model
- PMID: 22182693
- PMCID: PMC3674775
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.011
DHCEO accumulation is a critical mediator of pathophysiology in a Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome model
Abstract
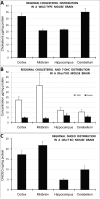
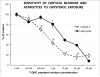
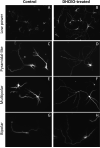
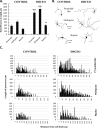
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS) is an inborn error of metabolism caused by defective cholesterol biosynthesis. Mutations within the gene encoding 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), the last enzyme in the pathway, lead to the accumulation of 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) in the brain tissue and blood of the SLOS patients. The objective of this study was to determine the consequences of the accumulation of an immediate cholesterol precursor, 7-DHC and its oxysterol metabolite, 3β,5α-dihydroxycholest-7-en-6-one (DHCEO), in the brain tissue of Dhcr7-KO mouse, a model for SLOS. We found that cholesterol, 7-DHC and DHCEO show region-specific distribution, suggesting that the midbrain and the cortex are the primary sites of vulnerability. We also report that neurons are ten fold more susceptible to a 7-DHC-derived oxysterol mixture than glial cells, and that DHCEO accelerates differentiation and arborization of cortical neurons. The overall results suggest that 7-DHC oxidative metabolites are critical contributors to altered neural development in SLOS. The future studies will test if antioxidant supplementation will ameliorate some of the clinical symptoms associated with this devastating disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An oxysterol biomarker for 7-dehydrocholesterol oxidation in cell/mouse models for Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.J Lipid Res. 2011 Jun;52(6):1222-1233. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M014498. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21402677 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant supplementation ameliorates molecular deficits in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Feb 1;75(3):215-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.06.013. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23896203 Free PMC article.
-
7-Dehydrocholesterol-derived oxysterols cause neurogenic defects in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.Elife. 2022 Sep 16;11:e67141. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67141. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36111785 Free PMC article.
-
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: Clinical, biochemical, and genetic insights with emerging treatment opportunities.Genet Med. 2025 Jul;27(7):101450. doi: 10.1016/j.gim.2025.101450. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Genet Med. 2025. PMID: 40314187 Review.
-
Mutational spectrum of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012 Nov 15;160C(4):263-84. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31346. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012. PMID: 23042628 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic Changes Associated with Loss of Cell Viability Induced by Oxysterol Treatment of a Retinal Photoreceptor-Derived Cell Line: An In Vitro Model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 26;22(5):2339. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052339. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33652836 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyzine Effects on Post-Lanosterol Biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome (SLOS) Models.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 10;15(4):562. doi: 10.3390/biom15040562. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305315 Free PMC article.
-
Metoprolol Inhibits Developmental Brain Sterol Biosynthesis in Mice.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 31;12(9):1211. doi: 10.3390/biom12091211. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139049 Free PMC article.
-
Natural inhibitor found for cell death by ferroptosis.Nature. 2024 Feb;626(7998):269-270. doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-00080-1. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38297047 No abstract available.
-
Oxysterols and Retinal Degeneration in a Rat Model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome: Implications for an Improved Therapeutic Intervention.Molecules. 2018 Oct 22;23(10):2720. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102720. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30360379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2001;12(2):105–112. - PubMed
-
- Korade Z, Mi Z, Portugal C, Schor NF. Expression and p75 neurotrophin receptor dependence of cholesterol synthetic enzymes in adult mouse brain. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28(10):1522–1531. - PubMed
-
- Irons M, Elias ER, Salen G, Tint GS, Batta AK. Defective cholesterol biosynthesis in Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Lancet. 1993;341(8857):1414. - PubMed
-
- Tierney E, Nwokoro NA, Kelley RI. Behavioral phenotype of RSH/Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2000;6(2):131–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

