Compartmental analysis of renal BOLD MRI data: introduction and validation
- PMID: 22183077
- PMCID: PMC3288694
- DOI: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e318234e75b
Compartmental analysis of renal BOLD MRI data: introduction and validation
Abstract
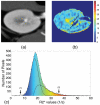
Objectives: Functional blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful tool to assess renal function, but BOLD analysis using T2* image differentiation of cortex and medulla is laborious and prone to errors. We developed and validated an alternative compartmental analysis method to differentiate renal cortical and medullary BOLD relaxivity index, R2*. This method uses whole-kidney regions of interest (ROI), thus eliminating the need for anatomic cortical and medullary definition.
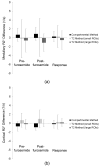
Materials and methods: Nine hypertensive patients and 11 domestic pigs, some with renal artery stenosis, were studied using BOLD MRI before and after injection of furosemide, which reduces medullary oxygen consumption. R2* in cortex and medulla estimated before and after furosemide with the compartmental method were compared with those obtained using conventional T2* image selection for ROI (manual ROI method), and a reference method with ROIs obtained using contrast-enhanced computerized tomography images were coregistered for the same kidneys.
Results: All 3 methods provided similar cortical R2* values, but the Bland-Altman methods' agreement confidence intervals of the reference and compartmental-derived medullary R2* response in humans and pigs were smaller than those in the manual ROI method. Operator dependency in swine was lower in the compartmental method, and its estimates of variation were almost 1/3 compared with the manual ROI method.
Conclusions: The new compartmental method, which is less labor intensive than the conventional method, provides comparable and less variable kidney R2* estimations, especially in renal medulla. This method could be useful for analysis of kidney BOLD data.
Figures




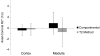

References
-
- Prasad PV, Edelman RR, Epstein FH. Noninvasive evaluation of intrarenal oxygenation with BOLD MRI. Circulation. 1996 Dec;94(12):3271–3275. - PubMed
-
- Epstein FH, Prasad P. Effects of furosemide on medullary oxygenation in younger and older subjects. Kidney Int. 2000 May;57(5):2080–2083. - PubMed
-
- Malvezzi P, Bricault I, Terrier N, Bayle F. Evaluation of intrarenal oxygenation by blood oxygen level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging in living kidney donors and their recipients: preliminary results. Transplant Proc. 2009 Mar;41(2):641–644. - PubMed
-
- Juillard L, Lerman LO, Kruger DG, et al. Blood oxygen level-dependent measurement of acute intra-renal ischemia. Kidney Int. 2004 Mar;65(3):944–950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

