The effects of artesunate on the expression of EGFR and ABCG2 in A549 human lung cancer cells and a xenograft model
- PMID: 22183882
- PMCID: PMC6264700
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules161210556
The effects of artesunate on the expression of EGFR and ABCG2 in A549 human lung cancer cells and a xenograft model
Abstract
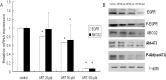
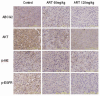
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Clinical and laboratory studies have suggested that multi-targeting approaches against neoplastic cells could help to increase patient survival and might reduce the emergence of cells that are resistant to single-target inhibitors. Artesunate (ART) is one of the most potent and rapidly acting antimalarial agents known, and it also exerts a profound cytotoxic activity toward cancer cells and reverses multi-drug resistance. In the present study, we found that artesunate inhibited NSCLC A549 cell growth and proliferation, induced apoptosis and suppressed tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner in A549 cells and a mouse xenograft model. Furthermore, artesunate down-regulated the expression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Akt and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 (ABCG2) at the mRNA and protein levels in vitro and in vivo. In conclusion, artesunate is an effective anti-cancer drug that may enhance the effectiveness of other anticancer drugs and may reverse multi-drug resistance by suppressing the transcription of ABCG2, which inhibits drug efflux.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation between adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette transporter G2 (ABCG2) and drug resistance of esophageal cancer and reversal of drug resistance by artesunate.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Sep;214(9):1467-1473. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30104076
-
Axitinib targeted cancer stemlike cells to enhance efficacy of chemotherapeutic drugs via inhibiting the drug transport function of ABCG2.Mol Med. 2012 Jul 18;18(1):887-98. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00444. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22549112 Free PMC article.
-
The EGFR pathway regulates BCRP expression in NSCLC cells: role of erlotinib.Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(14):1322-30. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666141205145620. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25479544
-
Lymecycline reverses acquired EGFR-TKI resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting GRB2.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:105007. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105007. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32561477
-
Anti-tumor mechanism of artesunate.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 25;15:1483049. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1483049. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39525639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artesunate inhibits proliferation and invasion of mouse hemangioendothelioma cells in vitro and of tumor growth in vivo.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):6170-6176. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6986. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113263 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-malarial drug, artemisinin and its derivatives for the treatment of respiratory diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Aug;158:104901. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104901. Epub 2020 May 13. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32405226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artesunate Enhances the Cytotoxicity of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Based Sonodynamic Therapy against Mouse Mammary Tumor Cells In Vitro.Molecules. 2017 Mar 27;22(4):533. doi: 10.3390/molecules22040533. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28346389 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate: A Review of Its Potential Therapeutic Effects and Mechanisms in Digestive Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 25;17(3):299. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030299. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 in combination with artesunate overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatoma cell and mouse models.J Ginseng Res. 2022 May;46(3):418-425. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35600776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fukuoka M., Yano S., Giaccone G., Tamura T., Nakagawa K., Douillard J.Y., Nishiwaki Y., Vansteenkiste J., Kudoh S., Rischin D., Eek R. Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected] J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;21:2237–2246. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.10.038. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lynch T.J., Bell D.W., Sordella R., Gurubhagavatula S., Okimoto R.A., Brannigan B.W., Harris P.L., Haserlat S.M., Jeffrey G., Supko J.G., Haluska F.G., et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa040938. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

