α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) expression in bone marrow-derived non-T cells is required for the inflammatory reflex
- PMID: 22183893
- PMCID: PMC3356417
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00405
α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR) expression in bone marrow-derived non-T cells is required for the inflammatory reflex
Abstract
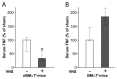
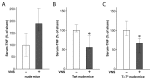
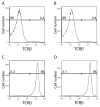
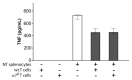
The immune response to infection or injury coordinates host defense and tissue repair, but also has the capacity to damage host tissues. Recent advances in understanding protective mechanisms have found neural circuits that suppress release of damaging cytokines. Stimulation of the vagus nerve protects from excessive cytokine production and ameliorates experimental inflammatory disease. This mechanism, the inflammatory reflex, requires the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR), a ligand-gated ion channel expressed on macrophages, lymphocytes, neurons and other cells. To investigate cell-specific function of α7nAChR in the inflammatory reflex, we created chimeric mice by cross-transferring bone marrow between wild-type (WT) and α7nAChR-deficient mice. Deficiency of α7nAChR in bone marrow-derived cells significantly impaired vagus nerve-mediated regulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), whereas α7nAChR deficiency in neurons and other cells had no significant effect. In agreement with recent work, the inflammatory reflex was not functional in nude mice, because functional T cells are required for the integrity of the pathway. To investigate the role of T-cell α7nAChR, we adoptively transferred α7nAChR-deficient or WT T cells to nude mice. Transfer of WT and α7nAChR-deficient T cells restored function, indicating that α7nAChR expression on T cells is not necessary for this pathway. Together, these results indicate that α7nAChR expression in bone marrow-derived non-T cells is required for the integrity of the inflammatory reflex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatic vagus nerve regulates Kupffer cell activation via α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug;52(8):965-976. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1304-z. Epub 2017 Jan 2. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28044208
-
A distinct vagal anti-inflammatory pathway modulates intestinal muscularis resident macrophages independent of the spleen.Gut. 2014 Jun;63(6):938-48. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304676. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Gut. 2014. PMID: 23929694
-
Role of the cholinergic nervous system in rheumatoid arthritis: aggravation of arthritis in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit gene knockout mice.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Sep;69(9):1717-23. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.118554. Epub 2010 May 28. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 20511609
-
Vagal Modulation of the Inflammatory Response in Sepsis.Int Rev Immunol. 2016 Sep 2;35(5):415-433. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2015.1127369. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Int Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27128144 Review.
-
Neuroimmune nexus in the pathophysiology and therapy of inflammatory disorders: Role of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2023 May;191:106758. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106758. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37028776 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of microglia and neurons by proinflammatory signaling following adolescent intermittent ethanol (AIE) exposure and in human AUD.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024 Mar 8;4:12094. doi: 10.3389/adar.2024.12094. eCollection 2024. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2024. PMID: 38524847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the efficacy of Transcutaneous Auricular Vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) in modulating local and systemic inflammation in experimental models of colitis.Bioelectron Med. 2024 Dec 9;10(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s42234-024-00162-5. Bioelectron Med. 2024. PMID: 39648211 Free PMC article.
-
T cells at the interface of neuroimmune communication.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Apr;153(4):894-903. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.10.026. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37952833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and pharmacological targeting of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor action blocks tumor progression in mouse models of breast cancer.J Immunol. 2025 Aug 1;214(8):2098-2111. doi: 10.1093/jimmun/vkaf148. J Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40653990
-
Overview of therapeutic applications of non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation: a motivation for novel treatments for systemic lupus erythematosus.Bioelectron Med. 2021 May 25;7(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s42234-021-00069-5. Bioelectron Med. 2021. PMID: 34030736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matsunaga K, Klein TW, Friedman H, Yamamoto Y. Involvement of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in suppression of antimicrobial activity and cytokine responses of alveolar macrophages to Legionella pneumophila infection by nicotine. J Immunol. 2001;167:6518–24. - PubMed
-
- Orr-Urtreger A, Kedmi M, Rosner S, Karmeli F, Rachmilewitz D. Increased severity of experimental colitis in alpha 5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit-deficient mice. Neuro-report. 2005;16:1123–7. - PubMed
-
- Giebelen IA, van Westerloo DJ, LaRosa GJ, de Vos AF, van der Poll T. Local stimulation of alpha7 cholinergic receptors inhibits LPS-induced TNF-alpha release in the mouse lung. Shock. 2007;28:700–3. - PubMed
-
- Pavlov VA, et al. Selective alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine endotoxemia and severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1139–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

