A phase 1, multicenter, open-label, dose escalation study of elotuzumab in patients with advanced multiple myeloma
- PMID: 22184404
- PMCID: PMC4467882
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-360552
A phase 1, multicenter, open-label, dose escalation study of elotuzumab in patients with advanced multiple myeloma
Abstract
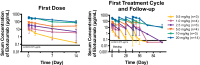
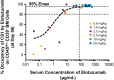
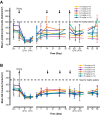
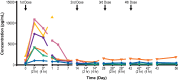
This multicenter, first-in-human study evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of the anti-CS1 monoclonal antibody elotuzumab. A standard 3 + 3 design was used to determine maximum tolerated dose; dose-limiting toxicities were assessed during cycle 1. Thirty-five patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma were treated with intravenous elotuzumab at doses ranging from 0.5 to 20 mg/kg every 2 weeks. Patients who achieved at least stable disease after 4 treatments could receive another 4 treatments. No maximum tolerated dose was identified up to the maximum planned dose of 20 mg/kg. The most common adverse events, regardless of attribution, were cough, headache, back pain, fever, and chills. Adverse events were generally mild to moderate in severity, and adverse events attributed to study medication were primarily infusion-related. Plasma elotuzumab levels and terminal half-life increased with dose whereas clearance decreased, suggesting target-mediated clearance. CS1 on bone marrow-derived plasma cells was reliably saturated (≥ 95%) at the 10-mg/kg and 20-mg/kg dose levels. Using the European Group for Bone and Marrow Transplantation myeloma response criteria, 9 patients (26.5%) had stable disease. In summary, elotuzumab was generally well tolerated in this population, justifying further exploration of this agent in combination regimens.
Figures
References
-
- Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(18):1860–1873. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2007. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; [Accessed April 13, 2011]. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2007. Based on November 2009 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER website, 2010.
-
- Alexander DD, Mink PJ, Adami H-O, et al. Multiple myeloma: a review of the epidemiologic literature. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(Suppl 12):40–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

