Severe isoniazid related sideroblastic anemia
- PMID: 22184524
- PMCID: PMC3238472
- DOI: 10.4081/hr.2011.e2
Severe isoniazid related sideroblastic anemia
Abstract
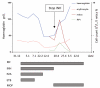
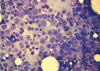
Isoniazid induced sideroblastic anemia is a rare event. We report case of a 45 year old Caucasian women with development of severe anaemia 4 month after introduction of Isoniazid as part of Tuberculosis treatment. While haemoglobin fell to 47 g/L and erythrocyte count to 1.5 G/L, reticulocytes were very low (reticulocyte production index of 0.48), but bone marrow aspirate showed an accelerated erythropoiesis with ringsideroblasts. Anaemia rapidly resolved after cessation of Isoniazid. We postulate an Isoniazid induced inhibition of the δ-Amino-levulinat-synthase resulting in marked depletion of heam synthesis.
Keywords: isoniazid; sideroblastic anaemia; tuberculosis..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin B6 responsive sideroblastic anaemia in a patient with tuberculosis.Br J Clin Pract. 1997 Jan-Feb;51(1):51-2. Br J Clin Pract. 1997. PMID: 9158274
-
Haem synthesis in sideroblastic anaemia.Br J Haematol. 1979 May;42(1):73-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb03699.x. Br J Haematol. 1979. PMID: 465361
-
Abnormal erythroid maturation in mice induced by isoniazid.Blood. 1975 Oct;46(4):625-9. Blood. 1975. PMID: 1174696
-
Recent advances in the understanding of inherited sideroblastic anaemia.Br J Haematol. 2008 Oct;143(1):27-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07290.x. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Br J Haematol. 2008. PMID: 18637800 Review.
-
Pyridoxine-refractory congenital sideroblastic anaemia with evidence for autosomal inheritance: exclusion of linkage to ALAS2 at Xp11.21 by polymorphism analysis.J Med Genet. 1994 Mar;31(3):213-8. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.3.213. J Med Genet. 1994. PMID: 7912287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondria and Iron: current questions.Expert Rev Hematol. 2017 Jan;10(1):65-79. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2016.1268047. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017. PMID: 27911100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sideroblastic anemia Secondary to anti-tubercular Therapy in a Patient with Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2025 Apr;41(2):447-448. doi: 10.1007/s12288-024-01824-9. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2025. PMID: 40224705 No abstract available.
-
Blood cytopenias as manifestations of inherited metabolic diseases: a narrative review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Feb 14;19(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03074-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38355710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Sideroblastic Anemia: An Overview of Genetics, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Current Therapeutic Options.J Blood Med. 2020 Sep 25;11:305-318. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S232644. eCollection 2020. J Blood Med. 2020. PMID: 33061728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquired myelodysplasia or myelodysplastic syndrome: clearing the fog.Adv Hematol. 2013;2013:309637. doi: 10.1155/2013/309637. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Adv Hematol. 2013. PMID: 24194760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krantz SB, Zaentz SD. Pure red cell aplasia. In: Gordon A.S, Silber R, LoBue J, editors. The year in Hematology. 1977. pp. 153–90.
-
- Matthes T. Sideroblastic anemias. Ther Umsch. 2006;63:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Sharp RA, Lowe JG, Johnston RN. Antituberculous drugs and sideroblastic anaemia. Br J Clin Pract. 1990;44:706–7. - PubMed
-
- MacCurdy RK, Simon ER. Thrombocytopenia and sideroblastic anemia with pyrazinoic acid amide (pyrazinamide) therapy. Chest. 1970;57:378–81. - PubMed
-
- Vives JF, Rouy JM, Wagner A, Vallat G. Anemia with hypersideroblastosis during anti-tuberculosis therapy. cure with vitamin therapy] Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1978;20:99–110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources