Severe isoniazid related sideroblastic anemia
- PMID: 22184524
- PMCID: PMC3238472
- DOI: 10.4081/hr.2011.e2
Severe isoniazid related sideroblastic anemia
Abstract
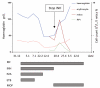
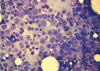
Isoniazid induced sideroblastic anemia is a rare event. We report case of a 45 year old Caucasian women with development of severe anaemia 4 month after introduction of Isoniazid as part of Tuberculosis treatment. While haemoglobin fell to 47 g/L and erythrocyte count to 1.5 G/L, reticulocytes were very low (reticulocyte production index of 0.48), but bone marrow aspirate showed an accelerated erythropoiesis with ringsideroblasts. Anaemia rapidly resolved after cessation of Isoniazid. We postulate an Isoniazid induced inhibition of the δ-Amino-levulinat-synthase resulting in marked depletion of heam synthesis.
Keywords: isoniazid; sideroblastic anaemia; tuberculosis..
Figures
References
-
- Krantz SB, Zaentz SD. Pure red cell aplasia. In: Gordon A.S, Silber R, LoBue J, editors. The year in Hematology. 1977. pp. 153–90.
-
- Matthes T. Sideroblastic anemias. Ther Umsch. 2006;63:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Sharp RA, Lowe JG, Johnston RN. Antituberculous drugs and sideroblastic anaemia. Br J Clin Pract. 1990;44:706–7. - PubMed
-
- MacCurdy RK, Simon ER. Thrombocytopenia and sideroblastic anemia with pyrazinoic acid amide (pyrazinamide) therapy. Chest. 1970;57:378–81. - PubMed
-
- Vives JF, Rouy JM, Wagner A, Vallat G. Anemia with hypersideroblastosis during anti-tuberculosis therapy. cure with vitamin therapy] Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1978;20:99–110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources