Long-term efficacy following readministration of an adeno-associated virus vector in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia
- PMID: 22185325
- PMCID: PMC4047999
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2011.106
Long-term efficacy following readministration of an adeno-associated virus vector in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia
Abstract
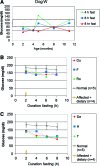
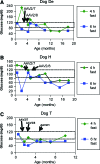
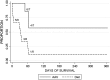
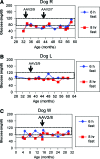
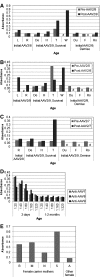
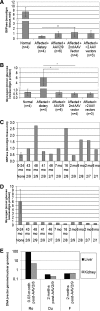
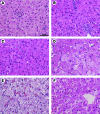
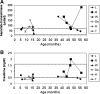
Glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD-Ia) is the inherited deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), primarily found in liver and kidney, which causes life-threatening hypoglycemia. Dogs with GSD-Ia were treated with double-stranded adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors encoding human G6Pase. Administration of an AAV9 pseudotyped (AAV2/9) vector to seven consecutive GSD-Ia neonates prevented hypoglycemia during fasting for up to 8 hr; however, efficacy eventually waned between 2 and 30 months of age, and readministration of a new pseudotype was eventually required to maintain control of hypoglycemia. Three of these dogs succumbed to acute hypoglycemia between 7 and 9 weeks of age; however, this demise could have been prevented by earlier readministration an AAV vector, as demonstrated by successful prevention of mortality of three dogs treated earlier in life. Over the course of this study, six out of nine dogs survived after readministration of an AAV vector. Of these, each dog required readministration on average every 9 months. However, two were not retreated until >34 months of age, while one with preexisting antibodies was re-treated three times in 10 months. Glycogen content was normalized in the liver following vector administration, and G6Pase activity was increased in the liver of vector-treated dogs in comparison with GSD-Ia dogs that received only with dietary treatment. G6Pase activity reached approximately 40% of normal in two female dogs following AAV2/9 vector administration. Elevated aspartate transaminase in absence of inflammation indicated that hepatocellular turnover in the liver might drive the loss of vector genomes. Survival was prolonged for up to 60 months in dogs treated by readministration, and all dogs treated by readministration continue to thrive despite the demonstrated risk for recurrent hypoglycemia and mortality from waning efficacy of the AAV2/9 vector. These preclinical data support the further translation of AAV vector-mediated gene therapy in GSD-Ia.
Figures
References
-
- Beaty R.M. Jackson M. Peterson D., et al. Delivery of glucose-6-phosphatase in a canine model for glycogen storage disease, type Ia, with adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors. Gene Ther. 2002;9:1015–1022. - PubMed
-
- Brix A.E. Howerth E.W. McConkie-Rosell A., et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ia in two littermate Maltese puppies. Vet. Pathol. 1995;32:460–465. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.T. Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver C.R., editor; Beaudet A.L., editor; Sly W.S., editor; Valle D., editor. The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001. pp. 1521–1551.
-
- Chen Y.T. Cornblath M. Sidbury J.B. Cornstarch therapy in type I glycogen-storage disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984;310:171–175. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.T. Bazzarre C.H. Lee M.M., et al. Type I glycogen storage disease: nine years of management with cornstarch. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1993;152(Suppl. 1):S56–S59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

