The nestin-expressing and non-expressing neurons in rat basal forebrain display different electrophysiological properties and project to hippocampus
- PMID: 22185478
- PMCID: PMC3282673
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-129
The nestin-expressing and non-expressing neurons in rat basal forebrain display different electrophysiological properties and project to hippocampus
Abstract
Background: Nestin-immunoreactive (nestin-ir) neurons have been identified in the medial septal/diagonal band complex (MS/DBB) of adult rat and human, but the significance of nestin expression in functional neurons is not clear. This study investigated electrophysiological properties and neurochemical phenotypes of nestin-expressing (nestin+) neurons using whole-cell recording combined with single-cell RT-PCR to explore the significance of nestin expression in functional MS/DBB neurons. The retrograde labelling and immunofluorescence were used to investigate the nestin+ neuron related circuit in the septo-hippocampal pathway.
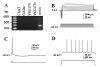
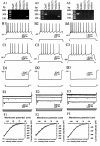
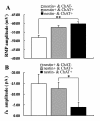
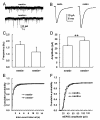
Results: The results of single-cell RT-PCR showed that 87.5% (35/40) of nestin+ cells expressed choline acetyltransferase mRNA (ChAT+), only 44.3% (35/79) of ChAT+ cells expressed nestin mRNA. Furthermore, none of the nestin+ cells expressed glutamic acid decarboxylases 67 (GAD(67)) or vesicular glutamate transporters (VGLUT) mRNA. All of the recorded nestin+ cells were excitable and demonstrated slow-firing properties, which were distinctive from those of GAD(67) or VGLUT mRNA-positive neurons. These results show that the MS/DBB cholinergic neurons could be divided into nestin-expressing cholinergic neurons (NEChs) and nestin non-expressing cholinergic neurons (NNChs). Interestingly, NEChs had higher excitability and received stronger spontaneous excitatory synaptic inputs than NNChs. Retrograde labelling combined with choline acetyltransferase and nestin immunofluorescence showed that both of the NEChs and NNChs projected to hippocampus.
Conclusions: These results suggest that there are two parallel cholinergic septo-hippocampal pathways that may have different functions. The significance of nestin expressing in functional neurons has been discussed.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Chemical identification of nestin-immunoreactive neurons in the rat basal forebrain: a re-examination.Neurochem Int. 2010 Apr;56(5):694-702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2010.02.005. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Neurochem Int. 2010. PMID: 20153393
-
Evidence for a distinct group of nestin-immunoreactive neurons within the basal forebrain of adult rats.Neuroscience. 2006 Nov 3;142(4):1209-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.07.059. Epub 2006 Sep 25. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16997483
-
Distinct electrophysiological properties of glutamatergic, cholinergic and GABAergic rat septohippocampal neurons: novel implications for hippocampal rhythmicity.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 15;551(Pt 3):927-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.046847. Epub 2003 Jul 15. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12865506 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary distribution of type 1 cannabinoid receptors and vesicular glutamate transporter 3 in basal forebrain suggests input-specific retrograde signalling by cholinergic neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Oct;18(7):1979-92. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02898.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14622230
-
Cholinergic modulation of hippocampal cells and circuits.J Physiol. 2005 Jan 1;562(Pt 1):81-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.076539. Epub 2004 Nov 4. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15528238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nerve Growth Factor Is Responsible for Exercise-Induced Recovery of Septohippocampal Cholinergic Structure and Function.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 1;12:773. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00773. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30443202 Free PMC article.
-
Special function of nestin(+) neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca in adult rats.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Feb 1;9(3):308-17. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.128229. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25206817 Free PMC article.
-
Nestin in immature embryonic neurons affects axon growth cone morphology and Semaphorin3a sensitivity.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 May 1;30(10):1214-1229. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-06-0361. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30840538 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise leads to the re-emergence of the cholinergic/nestin neuronal phenotype within the medial septum/diagonal band and subsequent rescue of both hippocampal ACh efflux and spatial behavior.Exp Neurol. 2016 Apr;278:62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26836322 Free PMC article.
-
Adolescent binge ethanol exposure alters specific forebrain cholinergic cell populations and leads to selective functional deficits in the prefrontal cortex.Neuroscience. 2017 Oct 11;361:129-143. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.013. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28807788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olton DS, Markowska A, Breckler SJ, Wenk GL, Pang KC, Koliatsos V. Individual differences in aging: behavioral and neural analyses. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991;4(1-2):166–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

