Trans-, cis-, and dihydro-resveratrol: a comparative study
- PMID: 22185600
- PMCID: PMC3313904
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-5-88
Trans-, cis-, and dihydro-resveratrol: a comparative study
Abstract
Background: Recent studies showed that moderate consumption of red or white wines increased the chances of breast cancer, while similar consumption of red wines, rich in trans-resveratrol (trans-R), decreased the rate of prostate cancer. This prompted us to explore the role of various forms of R in cancer proliferation.
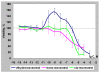
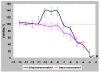
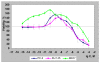
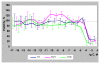
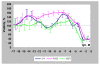
Results: Trans-R was found to be the most potent antiproliferative agent. Cis-R demonstrated somewhat less potency compared to trans-R. Unlike cis-R and trans-R, dihydro-R exhibits moderate proliferative effect on androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines PC-3 and DU-145 at picomolar concentrations. At higher concentrations, dihydro-R caused proliferation inhibition, similar to cis-R and trans-R. The proliferative effect of dihydro-R at low concentrations can be reversed by trans-R which acts as a partial antagonist in the presence of dihydro-R. Mixtures of dihydro-R and trans-R demonstrated complex non-monotonic cross-modulation activity patterns.
Conclusions: Dihydro-R exhibits proliferative effects in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells at picomolar and nanomolar concentrations. While the exact mechanism of these effects requires further evaluation, our preliminary results point to hormone receptor modulation activity. We also observed strong cross modulation between trans-R and dihydro-R at sub-picomolar concentrations. The role of dihydro-R in cancer proliferation related to moderate consumption of red wine remains an open question because dihydro-R has a very complex activity pattern in the presence of trans-R.
Figures
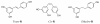
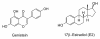
Similar articles
-
Dihydro-resveratrol--a potent dietary polyphenol.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Oct 15;20(20):6149-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20813524
-
Determination of stilbenes (delta-viniferin, trans-astringin, trans-piceid, cis- and trans-resveratrol, epsilon-viniferin) in Brazilian wines.J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Jul 13;53(14):5664-9. doi: 10.1021/jf050122g. J Agric Food Chem. 2005. PMID: 15998130
-
Profile of Stilbenes and Other Phenolics in Fanagoria White and Red Russian Wines.Metabolites. 2021 Apr 9;11(4):231. doi: 10.3390/metabo11040231. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33918825 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of cardioprotection by resveratrol, a phenolic antioxidant present in red wine (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2001 Jul;8(1):3-17. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.8.1.3. Int J Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11408943 Review.
-
Resveratrol and its analogs: defense against cancer, coronary disease and neurodegenerative maladies or just a fad?Mutat Res. 2008 Jan-Feb;658(1-2):68-94. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2007.08.004. Epub 2007 Aug 17. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 17890139 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Resveratrol Treatment on Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Alterations of Bcl-2 Family Members.Molecules. 2021 Oct 29;26(21):6560. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216560. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34770968 Free PMC article.
-
Dosis Facit Sanitatem-Concentration-Dependent Effects of Resveratrol on Mitochondria.Nutrients. 2017 Oct 13;9(10):1117. doi: 10.3390/nu9101117. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 29027961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Micro- and Nanocarriers for Resveratrol Delivery into and across the Skin in Different Skin Diseases-A Literature Review.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 26;13(4):451. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040451. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33810552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol in prostate diseases - a short review.Cent European J Urol. 2013;66(2):144-9. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2013.02.art8. Epub 2013 Aug 13. Cent European J Urol. 2013. PMID: 24579014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Delivery from Implanted Cyclodextrin Polymers Provides Sustained Antioxidant Effect on Implanted Neural Probes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 19;21(10):3579. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103579. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32438593 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

