Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces local inflammation of the rat carotid body via functional upregulation of proinflammatory cytokine pathways
- PMID: 22187044
- PMCID: PMC3278607
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-011-0900-5
Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces local inflammation of the rat carotid body via functional upregulation of proinflammatory cytokine pathways
Abstract
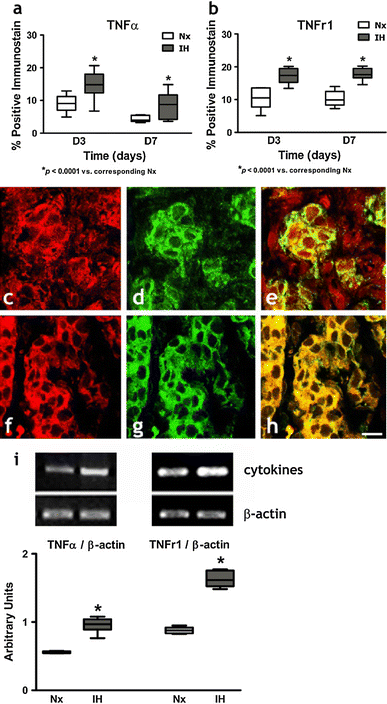
Maladaptive changes in the carotid body (CB) induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia (IH) account for the pathogenesis of cardiovascular morbidity in patients with sleep-disordered breathing. We postulated that the proinflammatory cytokines, namely interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and cytokine receptors (IL-1r1, gp130 and TNFr1) locally expressed in the rat CB play a pathophysiological role in IH-induced CB inflammation. Results showed increased levels of oxidative stress (serum 8-isoprostane and nitrotyrosine in the CB) in rats with 7-day IH treatment resembling recurrent apneic conditions when compared with the normoxic control. Local inflammation shown by the amount of ED1-containing cells (macrophage infiltration) and the gene transcripts of NADPH oxidase subunits (gp91(phox) and p22(phox)) and chemokines (MCP-1, CCR2, MIP-1α, MIP-1β and ICAM-1) in the CB were significantly more in the hypoxic group than in the control. In addition, the cytokines and receptors were expressed in the lobules of chemosensitive glomus cells containing tyrosine hydroxylase and the levels of expressions were significantly increased in the hypoxic group. Exogenous cytokines elevated the intracellular calcium ([Ca(2+)](i)) response to acute hypoxia in the dissociated glomus cells. The effect of cytokines on the [Ca(2+)](i) response was significantly greater in the hypoxic than in the normoxic group. Moreover, daily treatment of IH rats with anti-inflammatory drugs (dexamethasone or ibuprofen) attenuated the levels of oxidative stress, gp91(phox) expression and macrophage infiltration in the CB. Collectively, these results suggest that the upregulated expression of proinflammatory cytokine pathways could mediate the local inflammation and functional alteration of the CB under chronic IH conditions.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

