Integrating multiparametric prostate MRI into clinical practice
- PMID: 22187067
- PMCID: PMC3266575
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2011.9007
Integrating multiparametric prostate MRI into clinical practice
Abstract
Multifunctional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques are increasingly being used to address bottlenecks in prostate cancer patient management. These techniques yield qualitative, semi-quantitative and fully quantitative biomarkers that reflect on the underlying biological status of a tumour. If these techniques are to have a role in patient management, then standard methods of data acquisition, analysis and reporting have to be developed. Effective communication by the use of scoring systems, structured reporting and a graphical interface that matches prostate anatomy are key elements. Practical guidelines for integrating multiparametric MRI into clinical practice are presented.
Figures
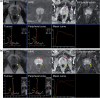

Similar articles
-
Interpretation and reporting multiparametric prostate MRI: a primer for residents and novices.Abdom Imaging. 2014 Oct;39(5):1036-51. doi: 10.1007/s00261-014-0097-x. Abdom Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24566965 Review.
-
[PI-RADS classification: structured reporting for MRI of the prostate].Rofo. 2013 Mar;185(3):253-61. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1330270. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Rofo. 2013. PMID: 23404430 German.
-
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of prostate cancer.Aktuelle Urol. 2014 Mar;45(2):119-26. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1371875. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Aktuelle Urol. 2014. PMID: 24700068 Review.
-
Prostate MRI based on PI-RADS version 2: how we review and report.Cancer Imaging. 2016 Apr 11;16:9. doi: 10.1186/s40644-016-0068-2. Cancer Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27067275 Free PMC article.
-
Risk stratification of prostate cancer: integrating multiparametric MRI, nomograms and biomarkers.Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(21):2417-2430. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0178. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27400645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The "PROCAINA (PROstate CAncer INdication Attitudes) Project" (Part II)--a survey among Italian radiation oncologists on radical radiotherapy in prostate cancer.Radiol Med. 2013 Oct;118(7):1220-39. doi: 10.1007/s11547-013-0925-z. Epub 2013 May 27. Radiol Med. 2013. PMID: 23716281
-
Potential of hybrid ¹⁸F-fluorocholine PET/MRI for prostate cancer imaging.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014 Sep;41(9):1744-55. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2786-7. Epub 2014 May 20. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24841413
-
Non-Invasive Prostate Cancer Characterization with Diffusion-Weighted MRI: Insight from In silico Studies of a Transgenic Mouse Model.Front Oncol. 2017 Dec 1;7:290. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00290. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29250485 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI of prostate cancer: an update on state-of-the-art techniques and their performance in detecting and localizing prostate cancer.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013 May;37(5):1035-54. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23860. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23606141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promise and pitfalls of quantitative imaging in oncology clinical trials.Magn Reson Imaging. 2012 Nov;30(9):1301-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.009. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22898682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Villeirs GM, De Meerleer GO, De Visschere PJ, Fonteyne VH, Verbaeys AC, Oosterlinck W. Combined magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in the assessment of high grade prostate carcinoma in patients with elevated PSA: a single-institution experience of 356 patients. Eur J Radiol. 2009;77:340–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.08.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
