Ocular findings in volcanic fog induced conjunctivitis
- PMID: 22187513
- PMCID: PMC3242421
Ocular findings in volcanic fog induced conjunctivitis
Abstract
Objective: To describe the ocular signs and symptoms of patients complaining of eye irritation due to volcanic fog (vog).
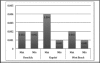
Methods: The study utilized a non-comparative, retrospective chart review of 30 patients who had a chief complaint of eye irritation, which the subjects attributed to vog. Ocular signs and symptoms are described and related to the ambient concentration of sulfur dioxide (SO(2)), particulate matter sized 2.5 microns (PM(2.5)), and vog visibility in O'ahu during the period of the study.
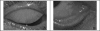
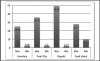
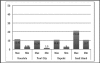
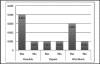
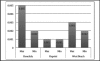
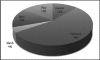
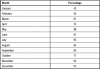
Results: Ocular signs noted were conjunctival injection (100%), clear mucous discharge (100%), papillary reaction (100%), punctal edema (80%), eyelid swelling (73.3%) and chemosis (63.3%). Ocular symptoms were itchiness (100%), foreign body sensation (100%), tearing (96.6%) and burning sensation (90%). All patients had concurrent respiratory symptoms. During the period of study, the highest 24-hour average concentration of particulate matter sized 2.5 microns (PM(2.5)) was 49.04 µg/m(3) and vog was visually present.
Conclusions: Patients complaining of eye irritation due to vog have observable ocular signs and symptoms.
Keywords: Particulate matter sized 2.5 microns (PM2.5); Sulfur dioxide (SO2); Vog induced conjunctivitis (VIC).
Figures


References
-
- Cadle RD, Laz'Arus AL, Shedlovsky JP. Comparison of Particles in the Fume from Eruptions of Kilauea, Mayon, and Arenal Volcanoes. Journal of Geophysical Research. 1969;74(13):3372–3378.
-
- Morrow JW. A Longitudinal Study to Characterize Hawaii's Volcanic Aerosol and Investigate its Potential Acute Effects on Asthmatic children. Manoa: University of Hawaii; 2000. Doctoral dissertation.
-
- Watson M, Rose WI. Retrieval of Information About Volcanic Plumes and Clouds Using the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Thermal Infrared Channels. Eos Transactions, American Geophysical Union Supplement. 2000;81(46):F1276.
-
- Chuan R. Characteristics of “VOG” from Kilauea Volcano, Hawai'i. In: Andres J R, editor. Volcano - Atmosphere Interactions Symposium Proceedings. Honolulu, Hawai'i: International Chemical Congress; 1995. pp. 1–6.
-
- Sutton J, Elias T, Hendley J, Stauffer . US Geological Survey Fact Sheet 169-97. Hawaiian Observatory, HI: U.S. Geological Survey; 2000. [May 2011]. Volcanic Air Pollution-A Hazard In Hawaii. [ http://pubs.usgs.goc/fs/fs169-97]

