A Population-Based Study of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome in Neonates Born between 37 and 43 Weeks of Gestation
- PMID: 22187569
- PMCID: PMC3236482
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/321545
A Population-Based Study of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome in Neonates Born between 37 and 43 Weeks of Gestation
Abstract
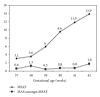
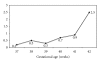
The epidemiology of meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) in term neonates is described in a population-based retrospective study of data recorded for all births from 2000 to 2007 in a French region (Burgundy). Of the 132 884 eligible term newborns, the rate of meconium-stained amniotic fluid (MSAF) was 7.93%. The prevalence of severe MAS was 0.067% in the overall population. MAS rate was 0.11% at 37-38 weeks of gestation (WG), 0.20% at 39-41 WG, and 0.49% at 42-43 WG. Factors independently associated with severe MAS were identified by a case-control study, that is, thick meconium amniotic fluid, fetal tachycardia, Apgar score ≤3 at 1 minute, and birth in a level III facility. Our results confirm the high prevalence of MSAF after 37 WG but also show the low frequency of severe MAS in a period corresponding to the new international recommendations on the management of birth with MSAF.
Figures
References
-
- Bhutani VK. Developing a systems approach to prevent meconium aspiration syndrome: lessons learned from multinational studies. Journal of Perinatology. 2008;28(3, supplement):S30–S35. - PubMed
-
- Goldsmith JP. Continuous positive airway pressure and conventional mechanical ventilation in the treatment of meconium aspiration syndrome. Journal of Perinatology. 2008;28(3):S49–S55. - PubMed
-
- Wiswell TE. Handling the meconium-stained infant. Seminars in Neonatology. 2001;6(3):225–231. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell SC, Moldenhauer J, Hassan SS, et al. Meconium aspiration syndrome in term neonates with normal acid-base status at delivery: is it different? American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2001;184(7):1422–1426. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

