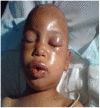
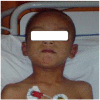
[Bite by a massive swarm of bees in a child]
- PMID: 22187598
- PMCID: PMC3224057
- DOI: 10.4314/pamj.v10i0.72225
[Bite by a massive swarm of bees in a child]
Abstract
Les piqûres multiples d'abeilles sont responsables d'envenimation sévère. Nous rapportons un cas d'une attaque massive par un essaim d'abeilles chez un enfant de sept ans. Sa gravité est liée à la localisation céphalique et au nombre important des piqûres qui était d'environ 270. Ses complications étaient l'insuffisance rénale, l'anémie et une conjonctivite. La prise en charge était symptomatique avec bonne évolution clinique et biologique.
Figures
References
-
- Limaiem R, Chaabouni A, El Maazi A, Mnasri H, Mghaieth F, El Matri L. Ocular lesions after bee sting of the cornea. A case report. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2009 Apr;32(4):277–9. - PubMed
-
- Kouamé EK, Brouh Y, Boua N. Honey bees massive poisoning in an infant. Arch Pediatr. 2004 Nov;11(11):1333–5. - PubMed
-
- Betten DP, Richardson WH, Tong TC, Clark RF. Massive Honey Bee Envenomation-Induced Rhabdomyolysis in an Adolescent. Pediatrics. 2006 Jan;117(1):231–5. - PubMed
-
- Bourgain C, Pauti MD, Fillastre JP, Godin M, François A, Leroy JP, Droy JM, Klotz F. Envennimation massive après piqure d'abeilles africaines. Pressemed. 1998;27:1099–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical