Participation of miR-200 in pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22189082
- PMCID: PMC3349843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.005
Participation of miR-200 in pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
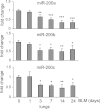
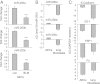
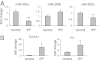
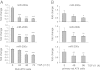
Excessive extracellular matrix production by fibroblasts in response to tissue injury contributes to fibrotic diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, involving transition of alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) to pulmonary fibroblasts, appears to be an important contributory process to lung fibrosis. Although aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRs) is involved in a variety of pathophysiologic processes, the role of miRs in fibrotic lung diseases is less well understood. In the present study, we found that miR-200a, miR-200b, and miR-200c are significantly down-regulated in the lungs of mice with experimental lung fibrosis. Levels of miR-200a and miR-200c were reduced in the lungs of patients with IPF. miR-200 had greater expression in AECs than in lung fibroblasts, and AECs from mice with experimental pulmonary fibrosis had diminished expression of miR-200. We found that the miR-200 family members inhibit transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of AECs. miR-200 family members can reverse the fibrogenic activity of pulmonary fibroblasts from mice with experimental pulmonary fibrosis and from patients with IPF. Indeed, the introduction of miR-200c diminishes experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Thus, the miR-200 family members participate importantly in fibrotic lung diseases and suggest that restoring miR-200 expression in the lungs may represent a novel therapeutic approach in treating pulmonary fibrotic diseases.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
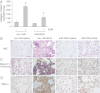
Figures
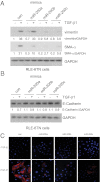
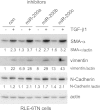
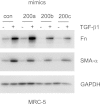
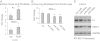
References
-
- Tomasek J.J., Gabbiani G., Hinz B., Chaponnier C., Brown R.A. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:349–363. - PubMed
-
- Thannickal V.J., Toews G.B., White E.S., Lynch J.P., 3rd, Martinez F.J. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Med. 2004;55:395–417. - PubMed
-
- Chapman H.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2011;73:413–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

