Development and implementation of explicit computerized protocols for mechanical ventilation in children
- PMID: 22189095
- PMCID: PMC3261103
- DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-1-51
Development and implementation of explicit computerized protocols for mechanical ventilation in children
Abstract
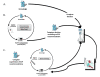
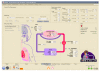
Mechanical ventilation can be perceived as a treatment with a very narrow therapeutic window, i.e., highly efficient but with considerable side effects if not used properly and in a timely manner. Protocols and guidelines have been designed to make mechanical ventilation safer and protective for the lung. However, variable effects and low compliance with use of written protocols have been reported repeatedly. Use of explicit computerized protocols for mechanical ventilation might very soon become a "must." Several closed loop systems are already on the market, and preliminary studies are showing promising results in providing patients with good quality ventilation and eventually weaning them faster from the ventilator. The present paper defines explicit computerized protocols for mechanical ventilation, describes how these protocols are designed, and reports the ones that are available on the market for children.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Closed loop mechanical ventilation.J Clin Monit Comput. 2014 Feb;28(1):49-56. doi: 10.1007/s10877-013-9465-2. Epub 2013 Apr 7. J Clin Monit Comput. 2014. PMID: 23564277
-
Computerized Decision Support Systems for Mechanical Ventilation in Children.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2016 Sep;5(3):95-100. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1568161. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2016. PMID: 31110892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Weaning children from mechanical ventilation with a computer-driven system (closed-loop protocol): a pilot study.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007 Sep;8(5):425-32. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000282157.77811.F9. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17693913 Clinical Trial.
-
Role responsibilities in mechanical ventilation and weaning in pediatric intensive care units: a national survey.Am J Crit Care. 2013 May;22(3):189-97. doi: 10.4037/ajcc2013784. Am J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23635928
-
Strategies for weaning from mechanical ventilation: a state of the art review.Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2015 Aug;31(4):189-95. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. 2015. PMID: 26209016 Review.
Cited by
-
A pilot prospective study on closed loop controlled ventilation and oxygenation in ventilated children during the weaning phase.Crit Care. 2012 May 16;16(3):R85. doi: 10.1186/cc11343. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 22591622 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Automated Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation after Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.Front Med (Lausanne). 2017 Mar 21;4:31. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2017.00031. eCollection 2017. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 28377920 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the global epidemiology of pediatric critical illness: the power, pitfalls, and practicalities of point prevalence studies.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014 Sep;15(7):660-666. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000156. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24751790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart Care™ versus respiratory physiotherapy-driven manual weaning for critically ill adult patients: a randomized controlled trial.Crit Care. 2015 Jun 11;19(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0978-6. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 26580673 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Closed loop mechanical ventilation.J Clin Monit Comput. 2014 Feb;28(1):49-56. doi: 10.1007/s10877-013-9465-2. Epub 2013 Apr 7. J Clin Monit Comput. 2014. PMID: 23564277
References
-
- Putensen C, Theuerkauf N, Zinserling J, Wrigge H, Pelosi P. Meta-analysis: ventilation strategies and outcomes of the acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:566–576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

