A pilot study of the efficacy of miglitol and sitagliptin for type 2 diabetes with a continuous glucose monitoring system and incretin-related markers
- PMID: 22189184
- PMCID: PMC3307032
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-115
A pilot study of the efficacy of miglitol and sitagliptin for type 2 diabetes with a continuous glucose monitoring system and incretin-related markers
Abstract
Background: Glucose fluctuations including robust postprandial hyperglycemia are a risk for promoting atherosclerosis and diabetic complications. The α-glucosidase inhibitors and the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have been found to effectively decrease postprandial hyperglycemia independently. Therefore, glycemic control with the combination of these drugs is warranted.
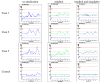
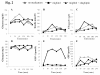
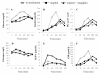
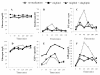
Methods: Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) was performed for 3 patients with type 2 diabetes and 1 control subject from the beginning to the end of the study. Medications were not administered to any of the subjects on the first day of the study. From the second day to the end of study (days 2-5), the subjects received miglitol (150 mg per day) and on days 4 and 5, sitagliptin (50 mg per day) was added to the treatment regimen. On the first, third, and fifth days of the study, blood was drawn at 0, 30, 60, 120, 180, and 240 min after breakfast for measurements of serum insulin, 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG), plasma glucagon, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP).
Results: Measurements of CGM and 1,5-AG levels showed that miglitol attenuated the escalation and fluctuation of glucose levels, and this was even more pronounced with the combination of miglitol and sitagliptin. The patterns of insulin secretion and glucagon secretion with miglitol alone or with a combination of miglitol and sitagliptin were various in the study subjects. Miglitol alone enhanced the release of GLP-1 in 1 patient with type 2 diabetes and the control subject, whereas the combination of miglitol and sitagliptin increased GLP-1 levels to varying degrees in all the subjects. Except for 1 subject, none of the subjects showed any change in GIP levels after the addition of sitagliptin, compared to the administration of miglitol alone.
Conclusions: In conclusion, CGM measurements revealed that a combination of the α-GI miglitol and the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin effectively reduced postprandial glucose fluctuation and stabilized blood glucose levels. Completely different response patterns of insulin, glucagon, GLP-1, and GIP were observed among the study subjects with either medication alone or in combination, suggesting that individual hormone-dependent glycemic responses to the α-GI and DPP-4 inhibitors are complicated and multifactorial.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cotreatment with the α-glucosidase inhibitor miglitol and DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin improves glycemic control and reduces the expressions of CVD risk factors in type 2 diabetic Japanese patients.Metabolism. 2014 Jun;63(6):746-53. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24559582 Clinical Trial.
-
Miglitol administered before breakfast increased plasma active glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels after lunch in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sitagliptin.Acta Diabetol. 2012 Jun;49(3):225-30. doi: 10.1007/s00592-011-0322-9. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Acta Diabetol. 2012. PMID: 21898126 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of miglitol, sitagliptin or their combination on plasma glucose, insulin and incretin levels in non-diabetic men.Endocr J. 2010;57(8):667-72. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k10e-103. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Endocr J. 2010. PMID: 20519806 Clinical Trial.
-
Sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a review of recent clinical trials.Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 Feb;24(2):489-96. doi: 10.1185/030079908x261069. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008. PMID: 18182122 Review.
-
Sitagliptin: Profile of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Drugs Today (Barc). 2007 Jan;43(1):13-25. doi: 10.1358/dot.2007.43.1.1043909. Drugs Today (Barc). 2007. PMID: 17315049 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of the addition of sitagliptin and miglitol on insulin-treated type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Ther. 2012 Nov;3(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s13300-012-0011-x. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Diabetes Ther. 2012. PMID: 23055336 Free PMC article.
-
Miglitol improves postprandial endothelial dysfunction in patients with acute coronary syndrome and new-onset postprandial hyperglycemia.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 Jun 19;12:92. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-92. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 23777506 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of green tea extract on insulin resistance and glucagon-like peptide 1 in patients with type 2 diabetes and lipid abnormalities: a randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled trial.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e91163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091163. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24614112 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of 24-week treatment with acarbose on glucagon-like peptide 1 in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients: a preliminary report.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013 May 4;12:73. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-73. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013. PMID: 23642288 Free PMC article.
-
1,5-Anhydroglucitol in diabetes mellitus.Endocrine. 2013 Feb;43(1):33-40. doi: 10.1007/s12020-012-9760-6. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Endocrine. 2013. PMID: 22847316 Review.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC Jr, Stone NJ. Coordinating Committee of the National Cholesterol Education Program. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;4:720–732. - PubMed
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Friday G, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O'Donnell CJ, Roger V, Rumsfeld J, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Hong Y. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee: Heart disease and stroke statistics--2007 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2007;115:e69–e171. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.179918. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gong Su, Mi Shuhua, Tao Hong, Li Zhao, Yang Hongxia, Zheng Hong, Zhou Yun, Ma Changsheng. Association of glycemic variability and the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2011;10:19. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

