Troponin T nuclear localization and its role in aging skeletal muscle
- PMID: 22189912
- PMCID: PMC3592954
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9368-4
Troponin T nuclear localization and its role in aging skeletal muscle
Abstract
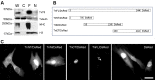
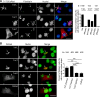
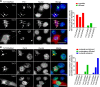
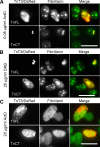
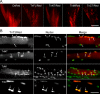
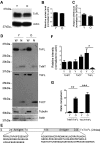
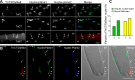
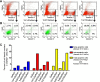
Troponin T (TnT) is known to mediate the interaction between Tn complex and tropomyosin (Tm), which is essential for calcium-activated striated muscle contraction. This regulatory function takes place in the myoplasm, where TnT binds Tm. However, recent findings of troponin I and Tm nuclear translocation in Drosophila and mammalian cells imply other roles for the Tn-Tm complex. We hypothesized that TnT plays a nonclassical role through nuclear translocation. Immunoblotting with different antibodies targeting the NH2- or COOH-terminal region uncovered a pool of fast skeletal muscle TnT3 localized in the nuclear fraction of mouse skeletal muscle as either an intact or fragmented protein. Construction of TnT3-DsRed fusion proteins led to the further observation that TnT3 fragments are closely related to nucleolus and RNA polymerase activity, suggesting a role for TnT3 in regulating transcription. Functionally, overexpression of TnT3 fragments produced significant defects in nuclear shape and caused high levels of apoptosis. Interestingly, nuclear TnT3 and its fragments were highly regulated by aging, thus creating a possible link between the deleterious effects of TnT3 and sarcopenia. We propose that changes in nuclear TnT3 and its fragments cause the number of myonuclei to decrease with age, contributing to muscle damage and wasting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calpain inhibition rescues troponin T3 fragmentation, increases Cav1.1, and enhances skeletal muscle force in aging sedentary mice.Aging Cell. 2016 Jun;15(3):488-98. doi: 10.1111/acel.12453. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Aging Cell. 2016. PMID: 26892246 Free PMC article.
-
Nonmyofilament-associated troponin T3 nuclear and nucleolar localization sequence and leucine zipper domain mediate muscle cell apoptosis.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013 Mar;70(3):134-47. doi: 10.1002/cm.21095. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 23378072 Free PMC article.
-
Troponin T3 associates with DNA consensus sequence that overlaps with p53 binding motifs.Exp Gerontol. 2018 Jul 15;108:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Exp Gerontol. 2018. PMID: 29596868 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution, Regulation, and Function of N-terminal Variable Region of Troponin T: Modulation of Muscle Contractility and Beyond.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016;321:1-28. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26811285 Review.
-
TNNT1, TNNT2, and TNNT3: Isoform genes, regulation, and structure-function relationships.Gene. 2016 May 10;582(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26774798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Troponin T3 regulates nuclear localization of the calcium channel Cavβ1a subunit in skeletal muscle.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Aug 15;336(2):276-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 15. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25981458 Free PMC article.
-
Type-1 pericytes accumulate after tissue injury and produce collagen in an organ-dependent manner.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Nov 6;5(6):122. doi: 10.1186/scrt512. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25376879 Free PMC article.
-
Potential cytotoxicity of truncated slow skeletal muscle troponin T (ssTnT) in a loss of function TNNT1 myopathy mouse model.FEBS J. 2025 Jun 26:10.1111/febs.70165. doi: 10.1111/febs.70165. Online ahead of print. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 40569886
-
Jack-of-many-trades: discovering new roles for troponin C.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(19):4553-4554. doi: 10.1113/JP276790. Epub 2018 Aug 28. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30084227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
BDA-410 Treatment Reduces Body Weight and Fat Content by Enhancing Lipolysis in Sedentary Senescent Mice.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017 Aug 1;72(8):1045-1053. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glw192. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27789616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbieri M, Ferrucci L, Ragno E, Corsi A, Bandinelli S, Bonafe M, Olivieri F, Giovagnetti S, Franceschi C, Guralnik JM, Paolisso G. Chronic inflammation and the effect of IGF-I on muscle strength and power in older persons. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003;284(3):E481–E487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
