Potentiation of the novel topoisomerase I inhibitor indenoisoquinoline LMP-400 by the cell checkpoint and Chk1-Chk2 inhibitor AZD7762
- PMID: 22189968
- PMCID: PMC3288175
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2579
Potentiation of the novel topoisomerase I inhibitor indenoisoquinoline LMP-400 by the cell checkpoint and Chk1-Chk2 inhibitor AZD7762
Erratum in
- Cancer Res. 2012 Apr 15;72(8):2153-4
- Cancer Res. 2014 Aug 1;74(15):4208
Abstract
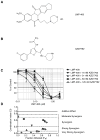
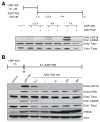
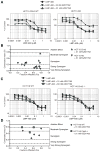
Novel topoisomerase I (Top1) inhibitors are in clinical development to circumvent the drawbacks of camptothecins (CPT). Here, we report molecular investigations into LMP-400, an indenoisoquinoline Top1 inhibitor in phase 1 clinical trial, by itself and in combination with the cell-cycle checkpoint inhibitor AZD7762. We examined drug effects on DNA replication and killing of cancer cells and found that LMP-400 showed synergistic antiproliferative activity when combined with AZD7762 in human colon carcinoma cells. Inhibition of S-phase progression and bromodeoxyuridine incorporation were similarly induced by LMP-400 and CPT and were abrogated by AZD7762. Replication studied by single DNA molecule analyses and immunofluorescence microscopy (molecular combing) showed rapid inhibition of fork progression in response to LMP-400 treatment with subsequent recapitulation after AZD7762 addition. AZD7762 inhibited both the activation/autophosphosphorylation of Chk1 and Chk2 at nanomolar concentrations in LMP-400-treated cells. This potent dual inhibition of Chk1 and Chk2 by AZD7762 was below the drug concentrations required to abrogate cell-cycle inhibition and produce synergism with LMP-400. Also, the synergism was independent of Chk2 both in Chk2-complemented cells and Chk2 knockout cells, suggesting additional mechanisms for cell-cycle abrogation by AZD7762. Together, our findings show a rationale for combining cell-cycle checkpoint inhibitors with the novel non-CPT indenoisoquinoline Top1 inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Checkpoint kinase inhibitor AZD7762 strongly sensitises urothelial carcinoma cells to gemcitabine.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 3;36(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0473-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28049532 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of radiosensitization by the Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762 involves abrogation of the G2 checkpoint and inhibition of homologous recombinational DNA repair.Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 15;70(12):4972-81. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3573. Epub 2010 May 25. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20501833 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-macrocalin B suppresses tumor growth in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and exhibits synergistic anti-cancer effects with the Chk1/2 inhibitor AZD7762.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 15;365:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30633885
-
Checkpoint kinase inhibitors: a patent review (2009 - 2010).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011 Aug;21(8):1191-210. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2011.586632. Epub 2011 May 20. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011. PMID: 21599421 Review.
-
Checkpoint kinase inhibitors: a review of the patent literature.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009 Feb;19(2):165-97. doi: 10.1517/13543770802653622. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009. PMID: 19441917 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer-Specific Synthetic Lethality between ATR and CHK1 Kinase Activities.Cell Rep. 2016 Jan 12;14(2):298-309. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.032. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26748709 Free PMC article.
-
ATR inhibitors VE-821 and VX-970 sensitize cancer cells to topoisomerase i inhibitors by disabling DNA replication initiation and fork elongation responses.Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 1;74(23):6968-79. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3369. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25269479 Free PMC article.
-
Combined inhibition of Wee1 and Chk1 gives synergistic DNA damage in S-phase due to distinct regulation of CDK activity and CDC45 loading.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):10966-10979. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14089. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28030798 Free PMC article.
-
NCI Comparative Oncology Program Testing of Non-Camptothecin Indenoisoquinoline Topoisomerase I Inhibitors in Naturally Occurring Canine Lymphoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 1;24(23):5830-5840. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1498. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30061364 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response pathways and cell cycle checkpoints in colorectal cancer: current concepts and future perspectives for targeted treatment.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012 May;12(4):356-71. doi: 10.2174/156800912800190901. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22385513 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

