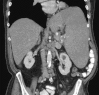
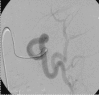
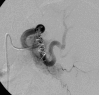
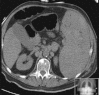
A fatal complication caused by occult pheochromocytoma after splenic artery embolization for malignant hypersplenism
- PMID: 22190248
- PMCID: PMC3396346
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-011-0307-7
A fatal complication caused by occult pheochromocytoma after splenic artery embolization for malignant hypersplenism
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial splenic embolization for the treatment of hypersplenism in tropical splenomegaly.Trop Doct. 1997 Apr;27(2):114-5. doi: 10.1177/004947559702700228. Trop Doct. 1997. PMID: 9133805 No abstract available.
-
Partial embolization as re-treatment of hypersplenism after unsuccessful splenic artery ligation.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 28;21(4):1365-70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1365. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25632215 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic artery embolization with detachable balloons for hypersplenism.J Int Med Res. 2018 Oct;46(10):4111-4119. doi: 10.1177/0300060518786419. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30027780 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Splenic Embolization.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Oct;205(4):720-5. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14637. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 26397320 Review.
-
Adverse Events Related to Partial Splenic Embolization for the Treatment of Hypersplenism: A Systematic Review.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020 Jul;31(7):1118-1131.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.08.015. Epub 2020 Feb 1. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32014400
Cited by
-
Lesson of the month 2: Blunt abdominal trauma: atypical presentation of phaeochromocytoma.Clin Med (Lond). 2018 Aug;18(4):345-347. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.18-4-345. Clin Med (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30072564 Free PMC article.
-
A System to Track Stent Location in the Human Body by Fusing Magnetometer and Accelerometer Measurements.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 19;23(10):4887. doi: 10.3390/s23104887. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37430804 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horton KM, Fishman EK. Multi-detector row CT of mesenteric ischemia: can it be done? Radiographics. 2001;21:1463–1473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

