Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly
- PMID: 22190361
- PMCID: PMC4004372
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.22516
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly
Abstract
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) results from deposition of β-amyloid in the media and adventitia of small arteries and capillaries of the leptomeninges and cerebral cortex and is a major cause of lobar intracerebral hemorrhage and cognitive impairment in the elderly. CAA is associated with a high prevalence of magnetic resonance imaging markers of small vessel disease, including cerebral microbleeds and white matter hyperintensities. Although advanced CAA is present in approximately ¼ of brains with Alzheimer disease (AD), fewer than half of CAA cases meet pathologic criteria for AD. This review will discuss the pathophysiology of CAA and focus on new imaging modalities and laboratory biomarkers that may aid in the clinical diagnosis of individuals with the disease.
Copyright © 2011 American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
A.V. has served as a consultant for Athena Diagnostics and has grants/grants pending from the NIH. S.M.G. has served as a consultant for Hoffman-La Roche, Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy, and Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and has received honoraria from Medtronic and Pfizer.
Figures
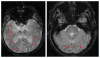
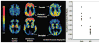
Comment in
-
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly.Ann Neurol. 2012 Apr;71(4):586; author reply 586. doi: 10.1002/ana.23564. Ann Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22522448 No abstract available.
References
-
- Viswanathan A, Greenberg SM. Chapter 38: Intracerebral hemorrhage. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;93:767–790. - PubMed
-
- Vinters HV. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy. A critical review. Stroke. 1987;18:311–324. - PubMed
-
- Jellinger KA. Alzheimer disease and cerebrovascular pathology: an update. J Neural Transm. 2002;109:813–836. - PubMed
-
- Ellis RJ, Olichney JM, Thal LJ, et al. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: the CERAD experience, Part XV. Neurology. 1996;46:1592–1596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

